Increasing Broadband Internet Penetration
In the OIC Member Countries
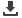
130
Company ADSL WiMAX
FTTH
3G
LTE
Oula
•
Part of the Saudi National
Fiber Network (17,000 kms)
•
98% coverage
•
HSPA+
•
FD-LTE over 1800
MHz
•
90% coverage
Zain
•
Over 2100
MHz band
•
HSPA+
•
FD-LTE over 1800
MHz
•
90% coverage
ITC
Yes
•
Yes
•
Part of the Saudi National
Fiber Network
Sources; Analysis Mason; Telegeography
Fixed and mobile broadband speeds and quality of broadband services
Despite the pervasive offering of fiber optic distribution, adoption of high speed fixed
broadband is still limited. Out of the 3.5 million lines deployed at the end of 2015, only 23%
were at speeds higher than 8 Mbps (see table 67).
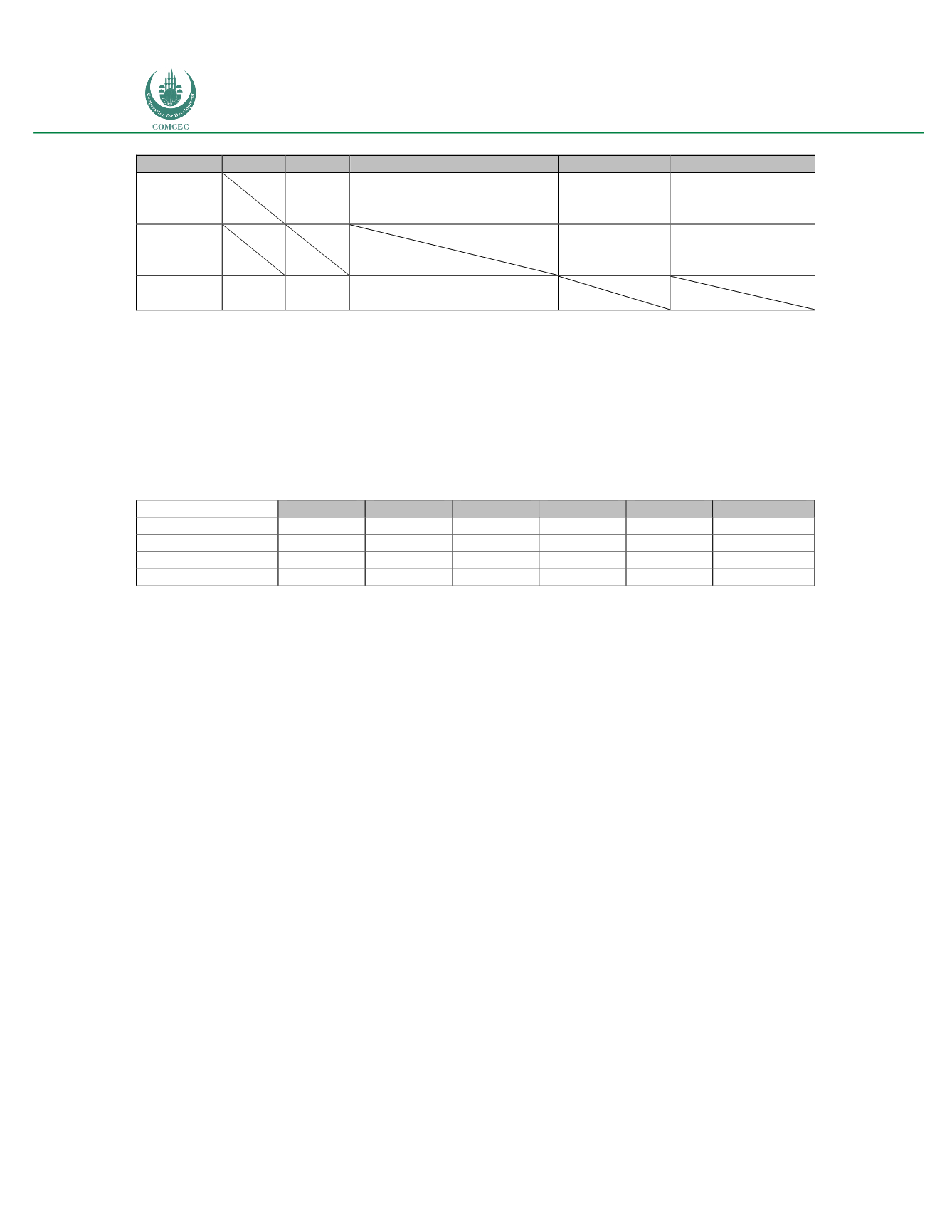
Table 67: Saudi Arabia: Line breakdown of fixed broadband speed (2011-2015)
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
CAGR
<2 Mbps (%)
39
35
33
39
36
14.2
2-8 Mbps (%)
57
55
49
42
41
6.6
8-20 Mbps (%)
4
9
16
17
20
71.3
>20 Mbps (%)
0
1
2
2
3
48.4
Source: CITC; MCIT Lab
This gap between supply of faster speeds and demand is due to four reasons:
•
Lack of local content and applications requiring faster broadband speeds
•
Limited fixed broadband quality of user experience
•
Relatively high prices for high speed broadband
•
Strong fixed mobile broadband substitution
As noted on table 67, 23 % of total fixed broadband lines offered a speed equal to or above 8
Mbps in 2015. It should be noted, however, that advertised speed does not equal real
performance. It is very common that, due to network quality issues or traffic saturation,
advertised speeds represent approximately 60% of real performance. For example, Akamai
reports that 50% of fixed broadband lines in Saudi Arabia actually only provide 4 Mbps
performance.
However, a comparison between Saudi Arabia statistics with other relevant countries provide
a relative context for understanding the country’s fixed broadband speed levels (see table 68).