Increasing Broadband Internet Penetration
In the OIC Member Countries
90
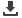
Country
(year of
survey)
Cost is too high Lack of
Digital
Literacy
Do not need
it or
“cultural
reason”
Privacy or
security
concern
Acces
Internet
elsewhere
Service is
not
available
(2014)
Iran (2013)
1.70
7.10
13.40
46.90
5.20
19.90
12.80
Morocco
(2014)
17.90 23.30
14.80
25.80
4.10
8.60
1.80
Oman (2013)
4.90
2.10
3.80
3.10
0.20
0.50
6.40
Qatar (2015)
0.60
0.40
0.20
2.30
1.50
Turkey (2013)
13.10 11.00
11.20
17.60
0.60
4.90
0.80
UAE (2014)
28.50
0
0
9.00
25.30
Source: Surveys compiled by the International Telecommunications Union. ITU World Telecommunications/ICT
Indicators Database 2016: ICT Households Access and Individual Use; indicator 17: Household without internet access by
type of reason.
As a confirmation of the adoption barriers discussed in chapter III, the survey data indicates
that, with the exception of handset cost in Qatar and the United Arab Emirates, limited
affordability represents an important barrier. While surveys for African countries are not
available, it is reasonable to assume that affordability represents a more important challenge
in that region. In addition to affordability, lack of digital literacy and cultural barriers also
represent an obstacle to broadband adoption.
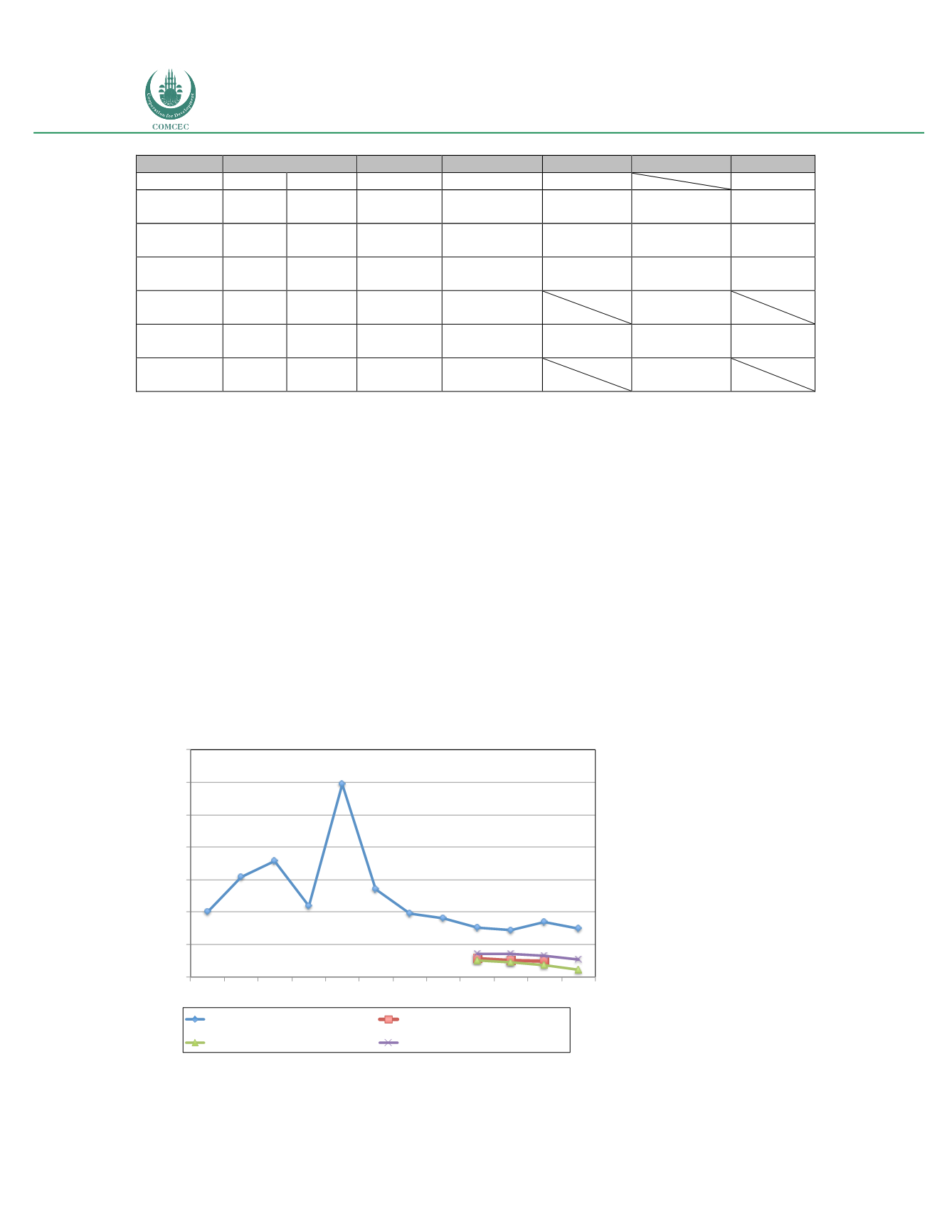
In light of these findings, it is pertinent to first examine what the general trend is with regards
to broadband pricing. If non-adopters cite pricing as an adoption barrier, how has pricing of
broadband evolved over the past years within the OIC Member Countries? Figure 24 presents
the average pricing of selected broadband products across the OIC Member Countries.
Figure 24: OIC Average: Pricing of selected broadband products
Sources: International Telecommunications Union; Telecom Advisory Services analysis
$0
$20
$40
$60
$80
$100
$120
$140
2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
Fixed Broadband
Mobile Broadband Postpaid
Mobile Broadband Prepaid
Mobile Broadband USB Postpaid