Increasing Broadband Internet Penetration
In the OIC Member Countries
87
Due to the limited statistics for fixed broadband coverage, the fixed broadband demand gap
can only be calculated for only few countries (see table 32).
Table 32: Selected OIC Member Countries: Fix d broadband demand gap (percent of
households) (2016)
Country
Fixed Broadband
Coverage (
%
)
Fixed Broadband
Penetration (
%
)
Demand Gap (
%
)
Benin
5.00
3.36
1.64
Cote d’Ivoire
20.00
4.00
16.00
Jordan
85.00
24.00
61.00
Kazakhstan
85.00
50.23
34.77
Saudi Arabia
80.00
77.56
2.44
Suriname
60.00
50.63
9.37
Source: Study survey and interviews
It is difficult to draw inferences from the fixed broadband demand gap. It would seem that in
the case of Suriname and Saudi Arabia (and Benin due to the low coverage), supply and
demand of fixed broadband have reached an equilibrium, while in the case of Cote d’Ivoire,
Kazakhstan and Jordan the demand gap is significantly high.
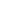
In the case of mobile broadband, as of 2015, penetration within the OIC Member Countries has
reached 29.41% of total population, compared to 87.17% in OECD countries. However, in this
case, the penetration growth trends indicate a slowing down among OECD countries (which
implies a gradual saturation) and an acceleration among the OIC Member Countries, which
reveals a convergence in adoption between both groups (see figure 23).
Figure 23: OECD versus OIC Member Countries: Mobile broadband penetration (2007-2015)
(percent of households)
Sources: International Telecommunications Union; Telecom Advisory Services analysis
Furthermore, mobile broadband penetration within the OIC Member Countries varies widely.
For example, penetration among Arab OIC Member Countries has reached 42.09%, while the
1%
9%
32%
45%
57%
67%
74%
81%
87%
0
0% 1%
6% 9% 11%
15%
23%
29%
0.00%
10.00%
20.00%
30.00%
40.00%
50.00%
60.00%
70.00%
80.00%
90.00%
100.00%
2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015
OECD OIC