
Improving Road Safety
in the OIC Member States
51
5
Road Safety Development Phases
5.1
Typical Road Safety Development Phases
In most countries that practice a Safe Systems Approach to road safety management or where
road safety management is traditionally high on the political agenda, i.e. have an active policy
for managing road safety effectively, there is a clear relationship between the road safety
initiatives and policies and the longer term effects on road safety
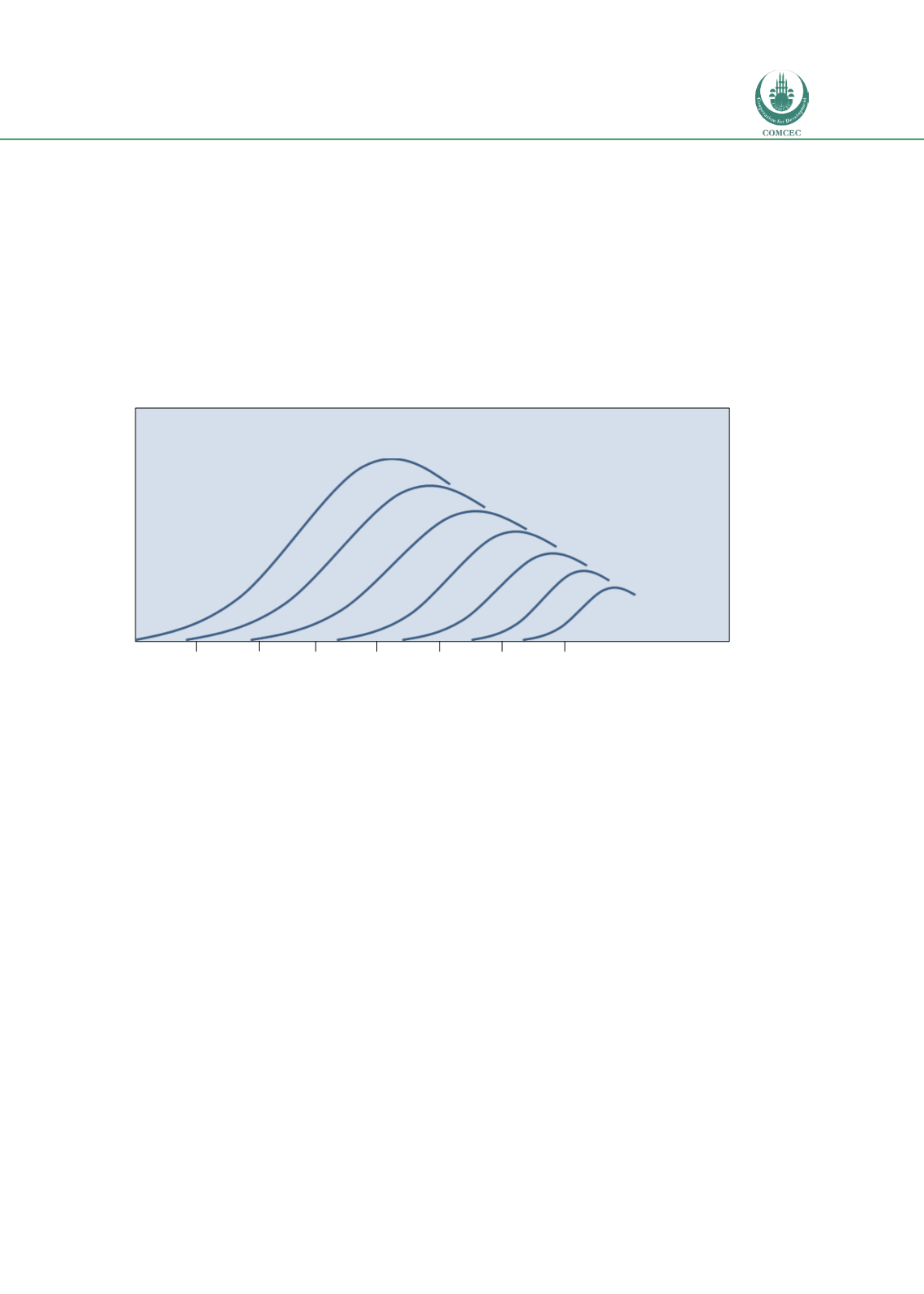
. Figure 9gives an example of
such policy developments in the Netherlands.
Figure 9: Policy development and investment into road safety improvements
Legislation
Motorway construction
Passive safety
Behavioural change
Decentralization
Sustainable safety
ITS application
1950
1960 1970 1980
1990
2000
2010
Investment in road safety
Road safety casualties
Source: SWOV
Figure 9illustrates three development phases (establishment, growth and consolidation) and
the level of investment required in these phases. Low investment is growing to a peak and
tapering off by which stage the next policy has taken up the same cycle. If one considers the right
vertical axis to represent the number of road deaths then the effect of an integrated approach to
policy development and implementation, backed by sustained investment (left vertical axis),
leads to a continual decrease in the number of fatalities and serious injuries. This figure also
illustrates that most new policy or technological development and implementation takes time
before an effect on road crashes can be established.
As an example, typically growing motorisation leads to an increased demand for improved road
infrastructure. However, this takes time to realise and before that is implemented road crashes
can be expected to increase before decreasing. Also important in this is that successful past
policies are not totally discarded, they become part of the new initiatives. In this way road safety
management evolves toward an integrated approach encompassing road users, roads and
vehicles and covering the traditional three E’s of engineering, enforcement and education. This
progression ultimately led to countries such as the Netherlands and Sweden adopting a holistic
approach which encapsulates all past thinking on road safety management into what today is
the Safe Systems Approach (avoid crashes and where they cannot be avoided, mitigate the injury
effect).
















