
Risk Management in Transport PPP Projects
In the Islamic Countries
60
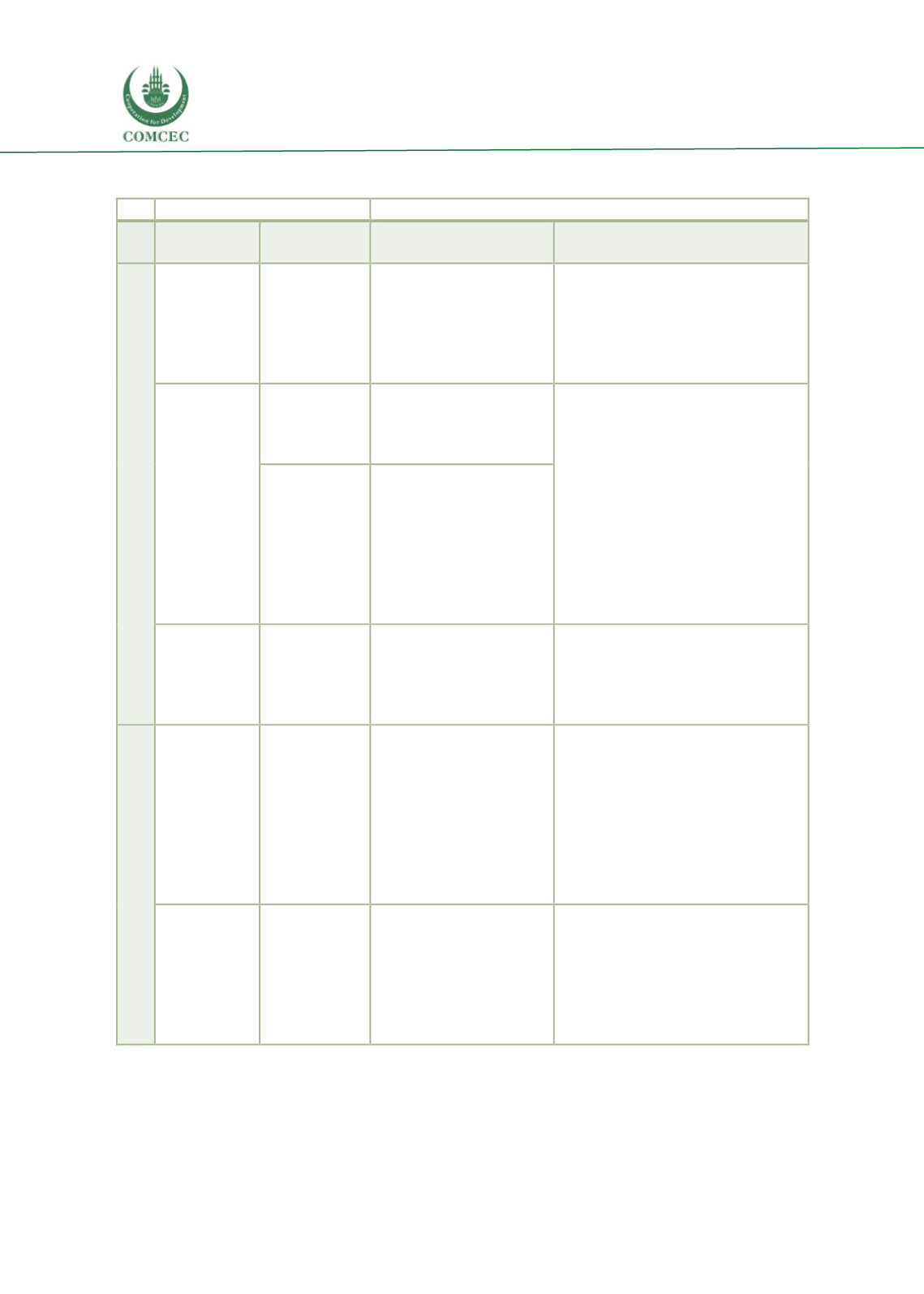
Table 16: Channels of transmission of the financial crisis
Risk threat and vulnerability
Risk Realization
Threat
Vulnerability
Effect on private
partners
Effect on the government
Financial
Interest rates
hike
Large
borrowing or
refinancing
need; variable
interest rates
Higher debt
service=increasing costs;
liquidity problems;
questionable feasibility of
some projects given lower
returns
Timing of investments (postponing);
trade-off between PPPs and
traditional concessions altered.
Possible cash flow support to
corporates
Unavailability
of credit
Underfinanced
project or new
project
Lowered capacity to
refinance; shorter loans;
shift to bonds and equity
vs. bank loans
Termination of existing projects,
failure to achieve financial close of
new projects; capital injections
Revenues
from the
project and/or
assets
securitized;
securities
indexed and
insured
Losses from downgrade of
bonds; lowered capacity
to refinance given lack of
insurers; shorter loans
and shift to bonds and
equity vs. bank loans
Decline in
stock market
prices
Companies do
not hold
sufficient
levels of their
capital in cash
Reduced capital of banks.
Reduced lending;
solvency problems and
recapitalization
Reduced investment for new and
existing PPPs and recapitalization
costs
Real
Exchange
rate
depreciation
Sizable
external debt,
currency
mismatches,
dollarization
Corporate balance sheets
if borrowing externally.
Counterbalancing:
increase in demand if
service is export oriented
(including highway).
Higher input costs if
inputs are imported.
Increased external debt service
(financing constraints) and lower
attractiveness for new investments
relying on external borrowing;
private sector defaults if widespread
dollarization; call of guarantees.
Counterbalancing force: switch from
foreign consumption to domestic
investment.
Slump in
domestic
demand
Commercial
projects
depending on
user fees and
explicit
contractual
guarantees
Corporate balance sheets
and pricing of credit by
financial partners;
liquidity problem;
contractor failure and
pressure to renegotiate.
Lower domestic revenue (financing
constraints) leading to lower
investment affecting new and old
PPPs; commercial projects risk; call
of guarantees due to decline in
fees/tolls; pressure to bail out failing
contractors and renegotiate.
Source: IMF (2009).
















