
Risk Management in Transport PPP Projects
In the Islamic Countries
38
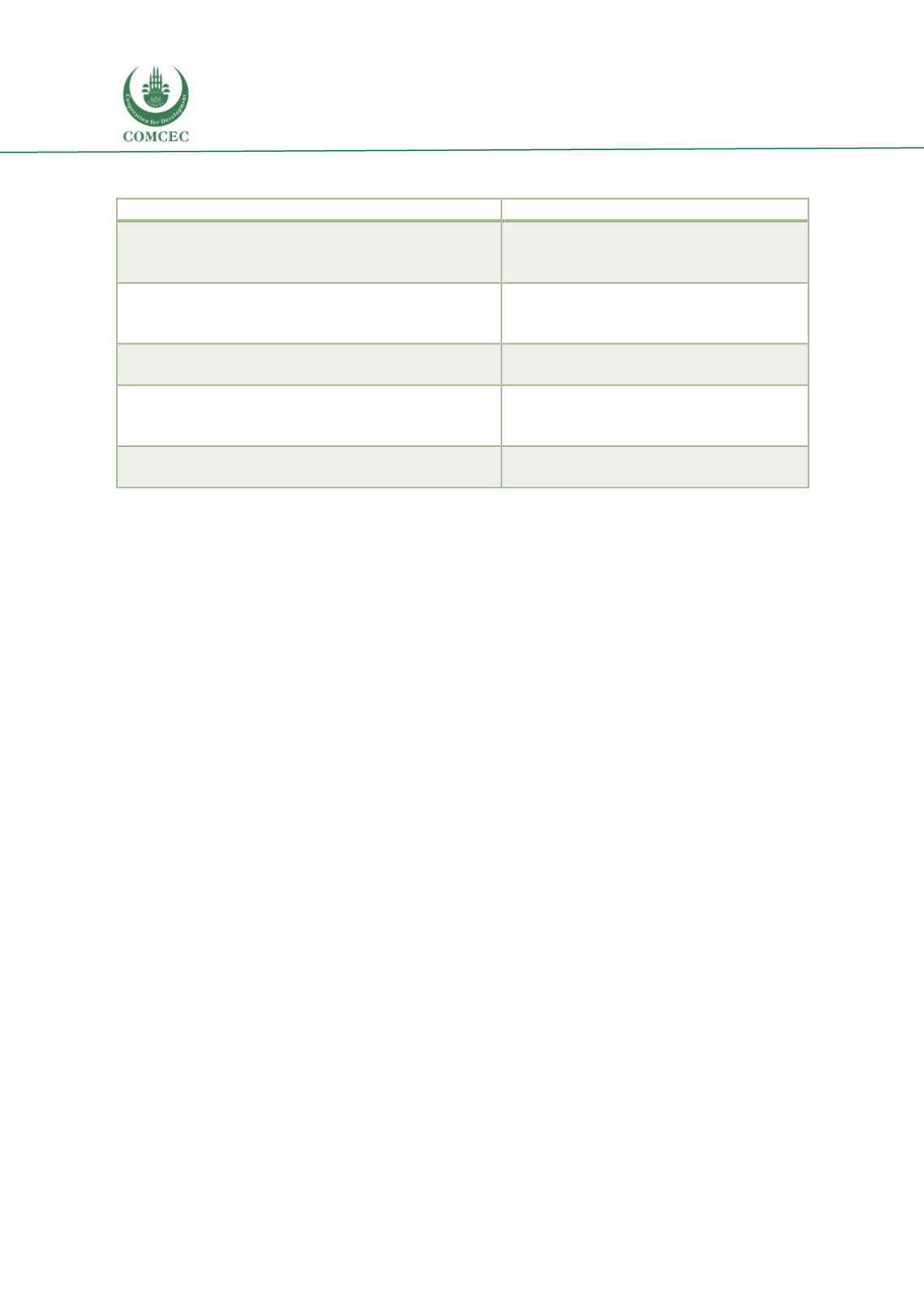
Table 8: Fit of Islamic finance and infrastructure PPP projects
Principles of Islamic finance
Infrastructure PPP project
Returns to Islamic financiers are linked to the
profit/earnings of an enterprise and derived from
commercial risk taken by the financier.
Infrastructure PPPs allow risk sharing among
the parties involved in the project, including
financiers.
Islamic financiers become partners in the project.
PPP projects allow Islamic financiers to
become parties to the project, not just mere
lenders.
Transactions are free from speculation or gambling
(“maysir”).
Infrastructure PPPs are by nature free from
speculation or gambling.
Excessive uncertainty in contracts (e.g. undetermined
price, time of delivery or subject matter) may be not
Shariah-compliant.
PPP contracts of infrastructure projects
generally include detailed clauses to minimize
uncertainty.
Investments relating to alcohol, drugs, gambling, weapons
and other prohibited activities are not permitted.
Infrastructures PPPs exclude these areas.
Source: Authors based on The World Bank, PPIAF and Islamic Development Bank, 2017.
The prohibition of excessive uncertainty or risk (“gharar”) in particular leads to a special
attention to
risk identification and risk assessment
, as an in-depth analysis of the risks is
especially necessary before stepping into the PPP process, for the latter to be Shariah-compliant.
Further, under Islamic principles whoever finances the operation needs to take the ownership
of the asset: this reduces the systemic risk and moral hazards associated with the conventional
risk transfer structures (The World Bank and IDB, 2018) and mitigates the risk of contract
violations arising from the agency conflict (Bowles, 2013). As profit is always connected with
assets onwhich it is generated and the transaction is not merely financial, speculation is avoided.
3.2.2.
Pre-tendering decision process
The second phase identified in the conceptual framework, i.e. Pre-tendering decision process,
has been divided into two elements: Screening for PPP suitability and Special arrangements for
PPPs. For each of the two elements, the following Table sets out relevant questions that guided
the analysis.
















