Planning of National Transport Infrastructure
In the Islamic Countries
67
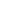
Sector
Project
Public transport
1.
Bayan Lepas LRT
2.
Ayer Itam Monorail
3.
Tanjung Tokong Monorail
4.
Raja Uda – Sg Nyiur – Buit Mertajam – Permatang Tinggi Monorail
5.
Tram
Highways
1.
Pan Island Link 1
2.
Pan Island Link 2 & 2A
Roads
1. North Coast Pair Road
Interchange (IC)
1.
Butterworth – Kulim Expresswa
2.
Juru IC
Missing Links and Road
Upgrading
1.
Pematang Pasir – Perda
2.
Bukit Minyak
BRT
1.
Permatang Tinggi – Batu Kawan line
Penang Undersea
Tunnel
1.
Phase 1
2.
Phase 2
3.
Phase 3
The state transport master plans in Malaysia seem to be driven by the respective regional
transport master plan (see Figure 16) rather than the national plan, which in this case is the
11MP. This is resulted by the fact that the regional transport master plan is the highest transport
sector plan, while the 11MP is a national development plan, not a national transport master plan.
3.2.3. Technical Factors
Like Nurly Zhol of Kazakhstan, 11 MP also has a 5-year planning horizon. As such, it is primarily
a list of approved infrastructure projects, not a visionary document that sets a framework for
the sector to develop. The (long term) vision of the NTI planning of Malaysia is a part of Vision
2020.
The transport infrastructure related initiatives are more prominent in the 10MP than in the
11MP. Among the initiatives are the developments of multimodal transport work, rail, maritime
and airport infrastructure.
Outcome-based approach
Malaysia is probably one of a few countries that implement an outcome-based approach for its
NTI plans. In the 11MP, the transport related outcome is “Improving road safety to reduce
accidents”, which is broken down into road fatalities index per 10,000 registered vehicles, as an
output. Furthermore, the NTI plans of Malaysia are developed based on a building block
approach in which the plan will serve as the foundation. This will be followed by the
development of analytical tools and guidelines for detailed implementation plans at the ground
level.