Planning of National Transport Infrastructure
In the Islamic Countries
44
2.8.2. Types of Evaluation and the Criteria Used
There are three types of evaluation that are commonly used:
1.
Ex-ante Evaluation
, that is applied before implementation to review the solutions
being proposed especially in mega projects as discussed by Priemus et al., (2008) and
ethical considerations (Van Wee and Roeser, 2013) also refer t
o Table 3where ex-ante
and ex-post evaluation results are compared for the French TGV system.
2.
Mid-termEvaluation
, that reviews the results of the project a few years after it is open
for business including environmental and economic impact (Tsamboulas and
Mikroudis, 2000) and of absorption of structural funding (Eser and Nussmueller,
2006).
3.
Ex-post Evaluation
, that looks back after many years on the performance of an entire
programme such as BRT in Bogota (Hidalgo et al., 2013) and EU Cohesion Funding
(Kelly et al., 2015).
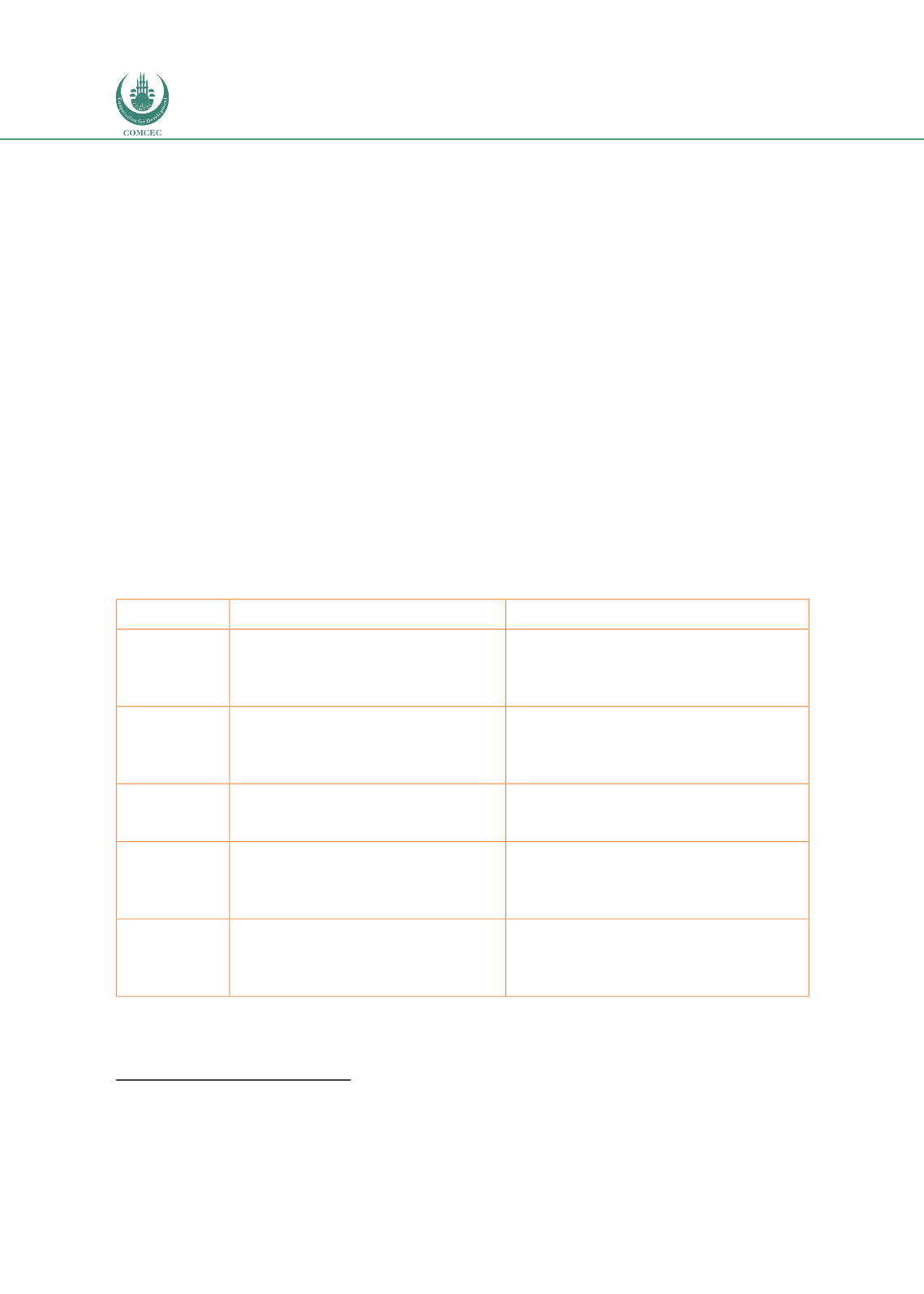
The most common criteria used in evaluation are as follows (OECD, 1991):
The application of weighting to the above criteria is a common sophistication. The main issue is
one of quantification and measurement of the criteria, resulting in the scoring on a rating scale.
Table 4: Criteria used in evaluation
Criteria
Measurement of the Criteria
Scoring
Relevance
Is the rationale for the intervention
still adequate (priority and validity)?
Use the Likert scale
13
1 - Not relevant or
aligned to policy any more: 5 - Highly
relevant and fully aligned to policy.
Average scores for all parameters
Efficiency
Has the project been cost-effective?
Has
implementing
the
intervention/s been as expected?
<10% of targets score 5, ie. of budget,
time line or km planned If > 100% score
1. Average score for all efficiency
attributes to provide the total score.
Effectiveness Have the project goals / results
expected being achieved?
Use Likert Scale: If meeting achieving
result score 5 if not 1. Average for all
results.
Sustainability Are these results able to be obtained
over time, are they likely to endure?
If budget, resources and capacity
adequate score 5: if not at all score 1…
scale in between. Average for all
attributes.
Wider
Impacts
Has the intervention positively
influenced cross cutting issues?
Use Likert scale, strongly agree that
project has created wider impact 5:
strongly disagree that it has not 1.
Average for all impacts.
13
Developed in 1932 by Rensis Likert to measure attitudes, the typical Likert scale is a 5 point ordinal scale used by
respondents to rate the degree to which they agree or disagree with a statement