Improving Customs Transit Systems
In the Islamic Countries
112
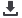
Other border controls supported by a risk management
system
48.90%
48.90%
2.20%
Possibility to provide additional trade facilitation measures to
operators meeting specified criteria (authorized operators)
48.90%
31.10%
20.00%
Transparency of the criteria for qualifying as an Authorized
Operator and the procedures for submission and review of
applications for AO status
66.70%
20.00%
13.30%
Adjustment of working hours of Customs personnel to
commercial needs
11.10%
22.20%
66.70%
Source: WTO TFA indicators database
3.2.5.7
Border Agency Cooperation at National Level
In only 6.6% of the countries there is an explicit co-ordination strategy led at a high political
level, while in 86.7% of the countries co-operation, co-ordination, exchange of information and
mutual assistance involve substantially all domestic agencies involved in the management of
cross border trade. Only 15.6% of the countries have institutionalized regional meetings to
develop a strategy and oversee implementation of border agency co-operation, and the
proceedings are publicly available, while 51.1% even have regular meetings, the information is
not available publicly. Still, there are 33.3% of the countries don’t have meetings between the
different public agencies involved, or such meetings are only ad hoc basis. In more than a half
OIC MS, data requirements of various border agencies are not coordinated /harmonized, and in
only 2.2% of the countries data requirements are coordinated/harmonized, and single data
entry is possible for traders. Also, only 2.2% of the MS are interconnected or have shared
computer systems where data is available in real-time. In 80% of the MS, there are no
interconnected or shared computer systems and no exchange of data on the national level
(among agencies involved in the management of cross border trade). In 86.7% of the OIC MS,
there is informal and ad hoc co-ordination to address contingencies, but in only 6.7% of the
countries there is a single location and coordinated timing is established for the physical
inspection of consignments by the various concerned agencies. Likewise, 91.1% of countries do
not share the inspection results with the agencies involved in the management of cross border
trade. When it comes to cooperation regarding risk management, in 68.9% of countries national
agencies involved in the management of cross border trade maintain separate risk management
mechanisms, while in only 4.4% there is interagency synergies in terms of risk analysis and
shared data and risk profiling of goods. In almost half of the countries, each agency certifies its
own AEOs and does not share infrastructure and equipment.