Improving the Border Agency Cooperation
Among the OIC Member States for Facilitating Trade
87
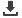
Figure 19. Map of Malaysia with major border crossing points
Source Wikimedia and CBRA analysis
156
Trade statistics and key indicators
Malaysia has a rather diversified export-driven economy characterised by strong high-tech and
tourism industries. In 2015, Malaysia had GDP of 296 BUSD that puts the country on the 35
th
place among the world’s nations. Malaysian GDP per capita is 25,100 USD, which is the second
highest among the Asian OIC member states (after Brunei). Malaysia has large oil and gas
reserves, and the country is a net exporter with a substantial trade surplus: in 2014, exports
totalled 224 BUSD and imports 189 BUSD.
The Malaysian economy relies heavily on exports that account for over 80% of the GDP.
Malaysia is the 19
th
largest exporter in the world and the third largest among the OIC member
states. In 2014, the most important Malaysian export commodities were integrated circuits
(40.7 BUSD), refined petroleum (24.7 BUSD), petroleum gas (21.3 BUSD), palm oil (12.3
BUSD), and telephones (11.6 BUSD). In total, machinery made 43% of the exports and mineral
products like petroleum accounted for 22%. Malaysia’s main export destinations are Singapore
(14 % of exports, 2014), China (12 %), the United States (10 %), Japan (10 %), Thailand (4.6
%), and Hong Kong (4.5 %).
The main import commodities into Malaysia in 2014 included integrated circuits (28.2 BUSD),
refined petroleum (22.2 BUSD), crude petroleum (7.3 BUSD), gold (3.2 BUSD), and planes,
helicopters and spacecraft (3.2 BUSD). The main origins of the imports to Malaysia are China
(18 % of imports, 2014), Singapore (13 %), Japan (7.2 %), the United States (7.1 %), Thailand
(6.0 %), and South Korea (4.2 %). The most important trading partner among the OIC member
states is the neighbouring Indonesia, which accounts for 3.9 % of Malaysian exports and 4.0 %
of imports. Malaysian trade has a heavy focus on Asia, since 67 % of exports and 71 % of
imports are with Asian partners.
Malaysia fares relatively well in global competitiveness rankings. The country ranks number
18 in the World Economic Forum’s Global Competitiveness Index (among 140 countries), and
number three among the OIC member states, after Qatar and the United Arab Emirates. In the
15
6 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Malaysia_location_map.svg (accessed 31.8.2016)
Port
Klang
Port TanjungPelepas
KualaLumpur
International Airport
Rantau Panjang/Kelantan
PadangBesar / Perlis
Bukit Kayu
Hitam / Kedah
Tebedu
Sungai Tujoh
Kuching
KualaLumpur
Indonesia
Thailand
Brunei
Indonesia
Singapore
Johor-Singaporecauseway