Preferential Trade Agreements and Trade Liberalization Efforts in the OIC Member States
With Special Emphasis on the TPS-OIC
64
gains of productivity are gained as a result of the specialisation obtained in each of the stages.
The concept of comparative advantage is associated less to products and more with country
actually applies. Where the bound tariff is greater than the applied tariff, than the country
could, in principle, resort to higher tariffs and protect domestic industry providing and remain
compatible with its WTO commitments, production stages and processes.
Although this phenomenon has lead to the notion of a "global factory" where firms located in
different parts of the world participate in production, the work of Baldwin (2011) and others
suggests that this phenomenon should not be characterised as "global"; that it is more accurate
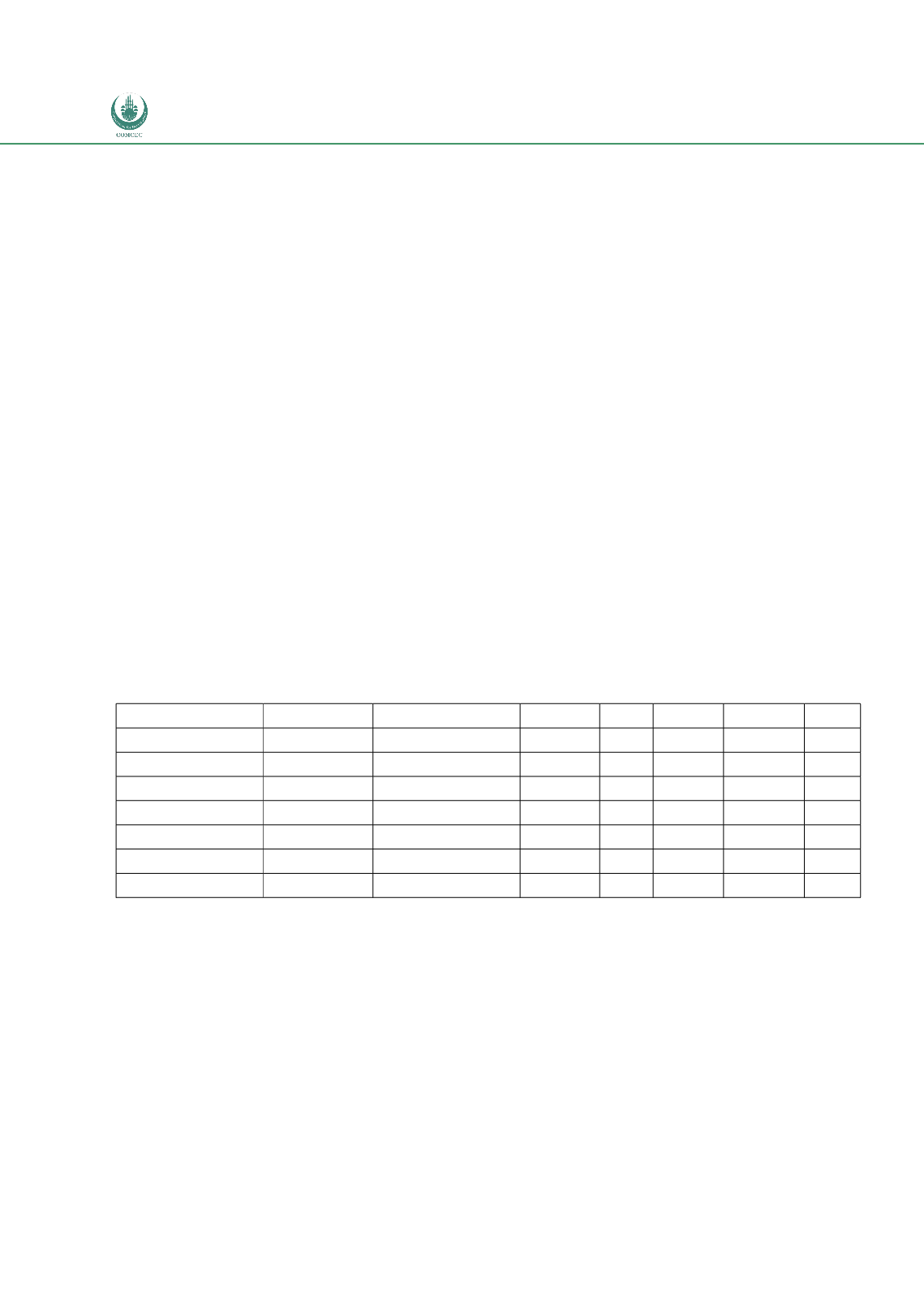
to see this as having a regional dimension. Table 6 presents the share of the exports of each
region to the others in the year 2007. It can be seen that the shares of intra-regional trade are
particularly high for North America, Europe and Asia, which reinforces the idea of regional
factories. Table 7 repeats this exercise using average data for the years 2012-13. However it
should be noted, that the numbers in Table 7 should be treated with some caution. Many
countries (notably several OIC countries) have not reported their trade for these years, and
therefore the shares are based only on the reporting countries. Hence the intra-regional
Middle East share in the former table is 12.9% while in the latter table the share is 23.9%. This
should not be read as saying that there has been a substantial rise in the intra-regional trade
share, because these numbers are being driven by the composition of the reporting countries,
rather than changes in intra-regional shares over time.
Table 6: Intra-regional Trade Flows (as % of Total Goods Exports, 2007)
Origin N America S & C America Europe CIS Africa M East Asia
N America
51.3
7
17.7
0.7
1.5
2.7
19
S & C America
30.5
24.9
21.5
1.5
2.8
1.9 16.7
Europe
7.9
1.9
73.7
3.5
2.6
2.7
7.6
CIS
4.8
1.7
56.2 20.6
1.5
3.5 11.7
Africa
22.7
3.9
39.5
0.9
9.9
2.8 19.7
M East
12.1
0.8
14.8
0.7
3.8
12.9 54.3
Asia
19.9
2.4
18.8
2.6
2.4
4 49.7
Source: Comtrade