Preferential Trade Agreements and Trade Liberalization Efforts in the OIC Member States
With Special Emphasis on the TPS-OIC
118
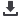
Figure 37:
Concentration of Exports by Product: Agadir Countries
Calculations based on 6 digit HS Comtrade data obtained via WITS.
An ex-ante assessment of the Agadir agreement using the gravity equation framework (Peridy,
2005) suggested extremely low intra-regional trade until early 2000s owing to large trade
costs. Reduction of these costs was considered as potentially enabling the rise in intra-
regional trade, although low trade complementarity between Agadir countries could limit
trade gains. Freund and Portugal-Perez (2012) identify the Agadir agreement as having
substantial trade effects, in line with average
effects observed for RTAs globally and in contrast
to the majority of other agreements involving countries in the Middle East and North Africa
region that often do not lead to substantial trade boost. Benassi et al (2013) explicitly ac- count
for concurrent trade liberalisation processes, especially between Agadir countries and the EU
(EuroMED agreements), between themselves, including the Agadir agreement, with other
countries, e.g. the US and unilateral tariff cuts. The key finding from this analysis is that trade
creation effects of an individual agreement are largely reduced by simultaneous reduction of
trade barriers with other countries. While trade creation effects are found to be limited, Agadir
countries do gain in terms of real income and these gains mainly owe to proliferation of
agreements: signing new RTAs offsets potential losses from being an excluded party in other
signed agreements.
Egypt-Turkey
The FTA between Egypt and Turkey was signed in December 2005 in Cairo and entered into
force early 2007. Turkey removed tariffs for industrial products at the moment of entry into
force of the agreement. Tariff cuts on the side of Egypt are adopted according to four different
lists, mirroring Egypt’s tariff schedules in the FTA with the EU. Tariffs for raw materials were