Preferential Trade Agreements and Trade Liberalization Efforts in the OIC Member States
With Special Emphasis on the TPS-OIC
122
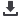
Figure 41:
Share of Egypt in Turkey’s Total Trade
Calculations based on Comtrade data
Gulf Cooperation Council
In December 2001, the members of the Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf
(GCC) Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and United Arab Emirates (UAE) signed the
Economic Agreement. It substantially revised the original Economic Agreement that was
originally signed in 1981, which laid down the ground for the economic relationship among
GCC members and established the GCC Free Trade Area. The 2001 agreement com- mitted to
create GCC customs union that as a minimum was meant to include a common external tariff
(CET), common customs regulations and procedures, single-entry point, elimination of all tariff
and non-tariff barriers, and national treatment provisions.
The GCC customs union commenced in 2003. There are no tariffs for goods circulation among
GCC members, but some products (around 1% of tariff lines) such as alcohol, pork, and related
products, etc. have a status of prohibited goods and cannot be traded (and produced) in GCC
countries. Members also generally have been applying the CET since 2003, although certain
differences remain until present, especially as regards treatment of prohibited and special
products (WTO, 2014a). The vast majority of tariff lines under GCC CET is set at 5%, with some
duty free lines. It is worth observing that at least for some countries (Saudi Arabia
-
see Table
21 below) adoption of the GCC CET implied substantial reduction of the average tariff
protection. Around 20 tariff lines on tobacco products are set at 100% or 100%/specific duty,
whichever is higher. For a number of tariff lines for "prohibited" and "special goods" there
remain differences in how these are applied between GCC countries (WTO, 2014a).