Enhancing Public Availability of Customs Information
In the Islamic Countries
1
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
With the entry into force of the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) on February 22
nd
,
2017, developing countries are more interested than ever in the full range of policy measures
that can reduce trade costs. In a competitive global environment where countries are eager to
attract trade and investment through Global Value Chains (GVCs), trade facilitation looms large
as an important part of the trade policy agenda.
In its broadest sense, trade facilitation is about reducing what economists refer to as “trade
costs”. That term refers to the full set of factors that drive a wedge between the producer price
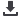
in the exporting country and the consumer price in the importing country. As the figure below
shows, trade costs can arise at different points in the value chain. Most research has focused on
explicit policy measures that increase trade costs, such as transport, time costs, and non-tariff
measures. But another potential source of trade costs is information costs: the fact that an
exporter must expend economic resources to understand the procedures that must be complied
with in order to enter a foreign market. Historically, foreign market entry has required advice
from local lawyers and trade professionals on issues as varied as customs formalities and
product standards. Even where information is publicly available, if it is not up to date and
complete, then exporters still need to engage additional costs before they can safely engage in
international trade transactions. The figure below shows the role of information costs in relation
to other sources of trade costs conceptually: information availability underlies many of the other
factors that contribute to high trade costs, and as such shows the potential for reducing trade
costs in a broad-based way by ensuring that high quality, complete, and up to date information
is publicly available.
Figure: Conceptual breakdown of international trade costs.
Source: Author.
The purpose of this report is to better understand the extent of public information availability
in OIC countries,, from the perspective of trade costs, and in particular to learn about ways in
which countries have successfully reduced those costs by promoting public information
availability. The starting point for the analysis is the TFA, specifically the first four articles that
deal with different aspects of information availability.
Between the Borders
• Transport costs
• Insurance costs
• Trade finance
At the Border
• Time cost of delays
• Formalities and
procedures
• Tariffs
• NTMs
Behind the Border
• NTMs applied
behind the border
• Other regulations
with trade impacts
• Distribution costs
Information Costs