
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
21
To rate the risk entity regarding one or more certification programs (such as an AEO
program, the partnership program, the key customer program);
To identify which of the risk entities need to be subjected to some form of control action,
as is the case in post-clearance audits and various types of quality assurance audits.
In the Customs context, both risk analyses have an important role to play. The strength comes
when transactional and behavioral risk analysis are connected into a unique, holistic risk
approach whereby the output of the one form of risk analysis (and the results of performing the
identified control measures) serves as input to the other form of risk analysis and vice versa. For
example, the transactional risk analysis of an import declaration is enhanced by being able to
draw on the behavioral risk rating of the trader which would be cumbersome, if not impossible,
to calculate on the fly if reasonable processing times for the real-time risk analysis are met. Due
to the fact that such trader risk ratings typically represent both a historical perspective (by
virtue of the historical data that is drawn upon) and a third party perspective (by virtue of the
third party data that is drawn upon), incorporating the behavioral risk rating into the real-time
risk assessment enhances another dimension to the analysis of the current event – and as such
import declarations that might have been scored in one way in isolation may reach a completely
different result. Likewise, the cumulative output of the risk analyses of all the import
declarations constitutes a behavioral pattern that can subsequently affect the risk rating of the
related traders. In the Customs context, one of the main purposes of using the transactional risk
analysis is for risk screening related with the goods in clearance process (including pre-
clearance): pre-arrival information (e.g., manifest) and customs declarations. The transactional
risk analysis determines the risk associated with the shipment (either at the level of the whole
shipment or on the individual consignment level) and the need for physical intervention.
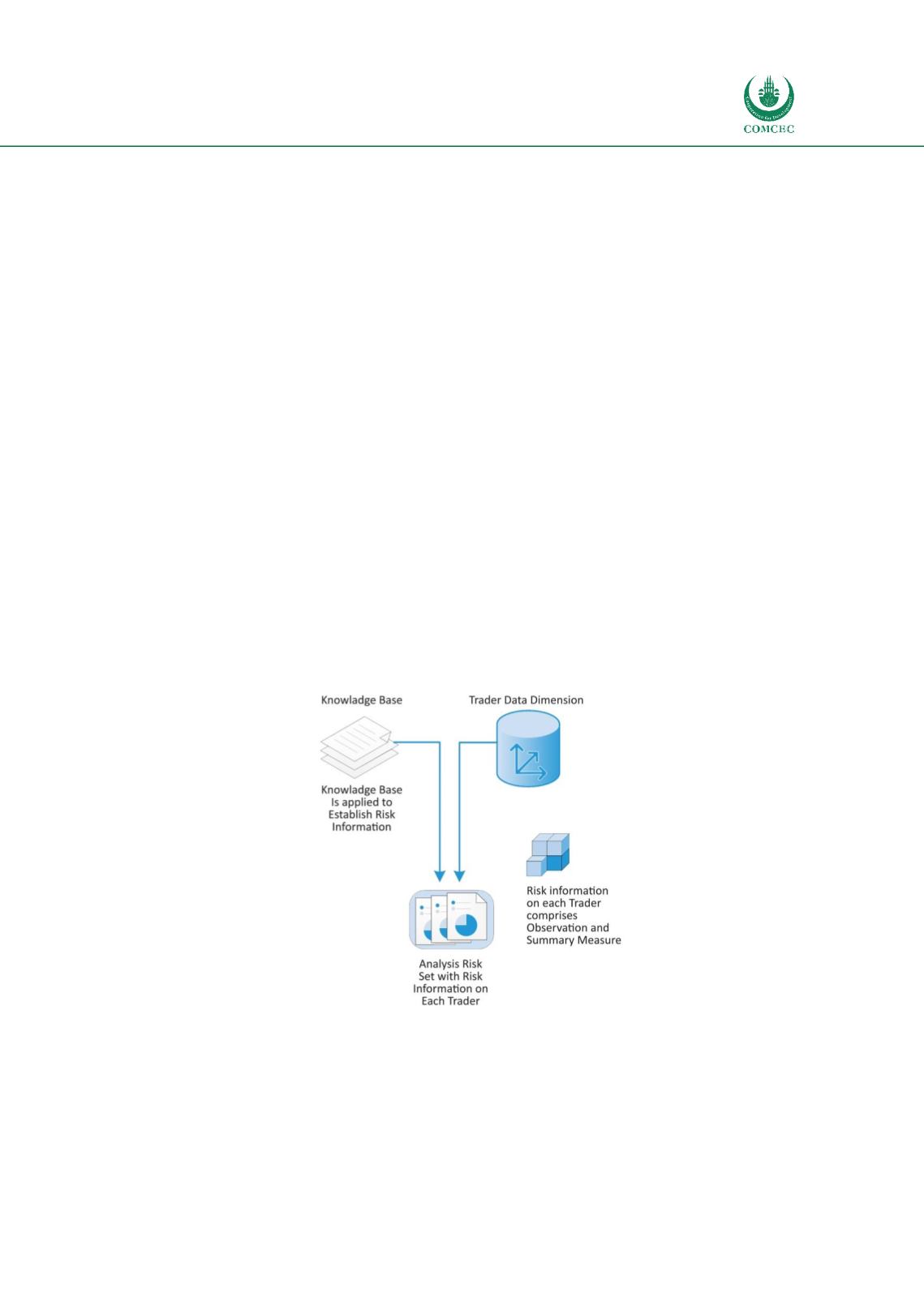
Figure 7: Behavioral Risk Analysis
Source: Author’s compilation
2.3
Benefits of Setting up CRMs
Risk management creates many benefits for the Government Authorities and the trading
community.
















