
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
20
requiring some form of intervention (e.g., a customs inspection) before the CRM cycle can
resume and those that do not require any intervention before the CRM cycle can resume. The
transactional risk module is tightly integrated, or “plugged into” the processing flow of the
corresponding part of the CDPS (e.g., clearance - import, export, etc.). As such, it is triggered (or
called) by the production system that needs the risk module to undertake a risk analysis, and
the risk module makes its output available back to the calling system in a suitable form.
In the Customs context, one of the main purposes of using the transactional risk analysis is for
risk screening related with the goods in clearance process (including pre-clearance): pre-arrival
information (e.g., manifest) and customs declarations. The transactional risk analysis
determines the risk associated with the shipment (either at the level of the whole shipment or
on the individual consignment level) and the need for physical intervention.
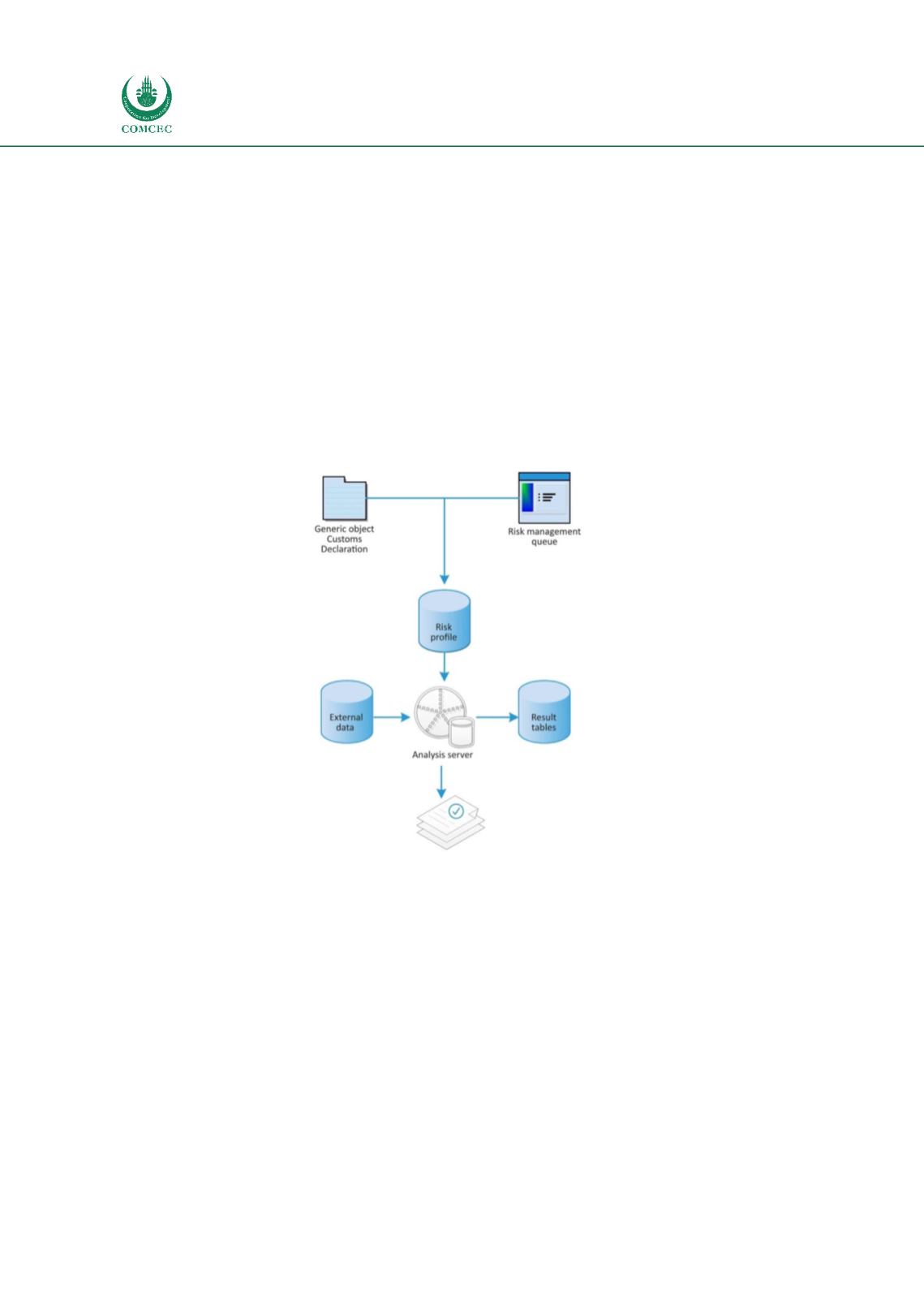
The overall composition of the transactional risk analysis module illustrated i
n Figure 6.Figure 6: Transactional Risk Analysis
Source: Author’s compilation
The objective of
behavioral risk analysis
is to undertake in-depth profiling of the risk entities
(e.g., traders, passengers, means of transport, etc.) from various risk perspectives, to supporting
a subsequent business process which is dependent on this risk rating (se
e Figure 7). The analysis
is performed on user request - either on an ad-hoc basis or according to some predetermined
schedule (e.g., when a trader first registers or at a particular time of the year). Behavioral risk
analysis is used for different purposes (with a separate dimension of risk being dedicated to
each purpose):
To provide qualifying input into the transactional risk analysis stage – for example, rules
in the transactional risk analysis stage often invoke a rating of the trader associated with
the transaction being analyzed to provide a greater level of precision in the transactional
analysis;
















