
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
18
2.2.2.3
Risk Evaluation and Prioritization
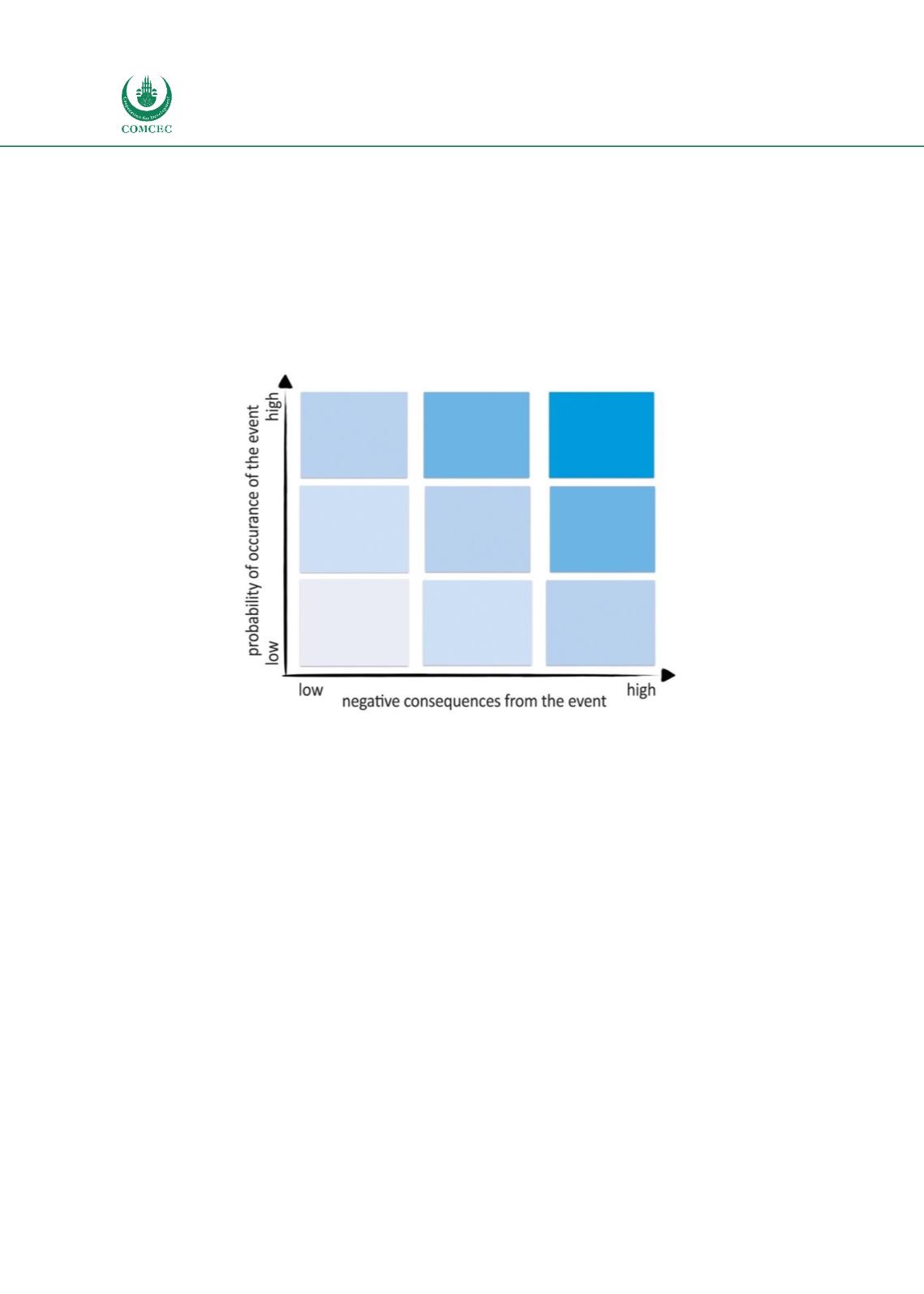
Risk evaluation and prioritization is the last stage in the risk assessment process and results in
the determination of risks as High (H), Medium (M), or Low (L) risks based on analyzed
probability and negative consequences (Figure 5). This stage of CRM cycle helps to focus
customs controls on areas with the highest risk while allowing the majority of trade to flow
relatively freely through customs. Depending on the assessment result, the decision stage will
define the type of control (physical, documentary, a posteriori) taking into account resources
and other constraints, including burdens on trade.
Figure 5: Risk levels based on probability and consequences of the event
Source: Author’s compilation
2.2.2.4
Preparation/Profiling
A risk profile is the means by which a CA puts risk assessment (the first three stages of the cycle)
into practice. Based on the results from the previous steps, profiling refers to linking risks to
certain types of shipments based on their risk level. Risk rules, commonly called risk profiles,
are used to evaluate information in a CD and supporting documents.
Risk profiles are rules based on observations of passengers, traders, goods, means of transport,
specific information from the international customs community, and predictive data analytics.
Any declaration is matching at least one of the risk profiles targeted for physical inspection
which is conducted according to recommended control measures. These rules are a logical
combination of two or more indicators, ranging from relatively simple to highly complex
algorithm. An example of a simple profile is: commodity code = equal to “xx” and country = equal
to “yy.” More complex rules typically combine several conditions or calculations. Most risk
profiles have a relatively short lifespan - from a few hours to a day or a week. Continuously
updating existing rules or defining new rules is vital for the effectiveness of CRM.
A risk profile should contain a description of the risk area, an assessment of the risk, the counter-
measures to be taken, an action date, the results, and an evaluation of the effectiveness of the
action taken. The counter-measures included in risk profiles are instructions on how to deal
with the particular shipment given the circumstance of the event. Such circumstances can
impact the treatment decision for a particular shipment.
















