
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
121
the authority, etc. The main objective stipulated in the CRM strategy is to decrease all types of
controls in the red channel by 15%.
The SCC has access to different sources including the FNID
75
, information fromUNODC and open
sources (internet, social networks, etc.). Software and databases used by SCS:
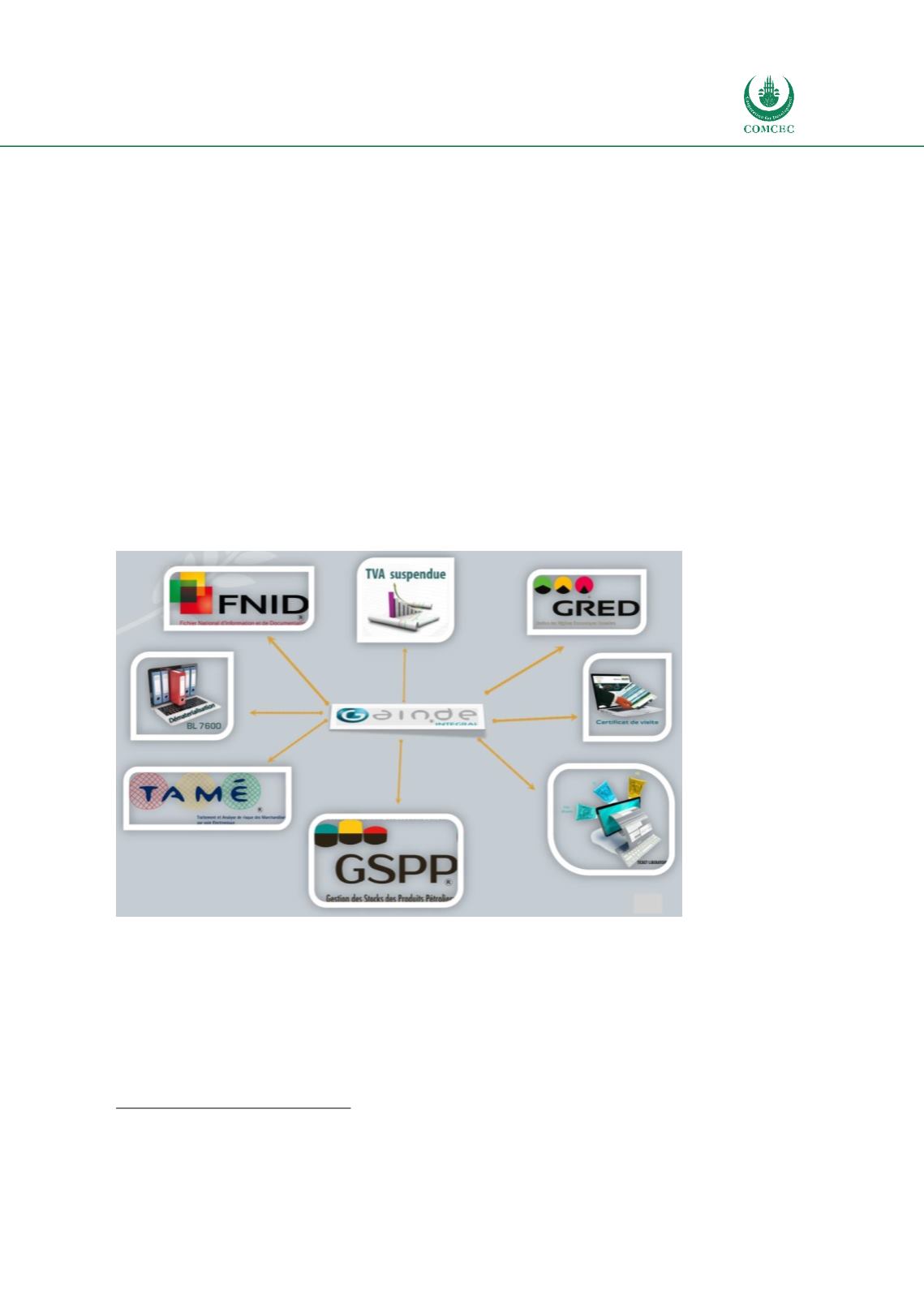
GAINDE Intégrale: CDPS constitutes the support for customs declarations, collection,
and payment of duties and taxes;
GAINDE extension: management of all internal customs procedures in customs
clearance offices: request for Post Clearance Audit, parcels, air/rail cargo manifest, etc.;
GAINDE DEMAT: gateway for exchanging permits and certificates managed by GANDE
2000 SW, pre-clearance documents (OGA’s), payments (banks), insurance, transporters,
etc.;
CDPS TAME: risk analysis, targeting and risk guidance;
FNID: National Information and Documentation System (FNID), a database for
management of information related to drugs, litigation, vessels and currency
declarations.
Figure 43: Senegalese Customs IT Systems
Source: Senegalese Customs presentation WCO IT Conference 2016
The Intelligence Unit is using the information available in WCO CEN and enters the data in the
TAME as needed. Currently, there is a pilot project for exchange of data with the Senegalese Tax
Administration, but for the time being, the tax information is not used systematically. The SCC is
planning to develop a common CRM IT System for the SW, customs and tax administrations.
Table 34compares the SCC CRM previous with its current approach:
75
National Information and Documentation File (FNID), database information, narcotics, litigation, ships and currency
declarations
















