Special Economic Zones in the OIC Region:
Learning from Experience
53
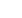
Zones
Fiscal Incentives
Non-fiscal Incentives
Ras Al Khaimah FTZ
0% import and re-export duties
0% personal income tax
Low land rates
No restrictions on employment
No restrictions on hiring of foreign
employees
Zero currency restrictions
Access to land through long-term
renewable leases
Source: BuroHappold Analysis 2017
A
s Table 4-3demonstrates, within the selected OIC SEZ case studies, a broad range of fiscal and
non-fiscal incentives are offered. It is observed that there are a number of common incentives
deployed to attract investments to SEZ, many of which have commonality with global
observations in SEZ development. The key regulatory, fiscal and financial incentives identified
in the above analysis are presented below:
Regulatory incentives:
o
Enhanced ability to employ foreign nationals; granting of visas and work permits;
o
Guarantees against nationalisation, expropriation and price controls;
o
Greater flexibility in repatriation of profits; and
o
Higher share of foreign business ownership.
Fiscal Incentives:
o
Exemption from corporate and personal income tax;
o
Reductions in customs duties, import/export tariffs and VAT on items related to
investment; and
o
Income tax exemption (mostly for an extended duration of ~5-15 years).
Financial Incentives:
o
State financed infrastructure;
o
Repatriation of profits;
o
Soft loans from national development banks; and
o
Preferential rates for land and utilities.
4.3
Evaluation of SEZ Development in OIC Member Countries
The following matrix provides a comparison of the SEZs selected for the comparative and
competitive benchmarking exercise including additional factors such as cost of energy and
competitive advantage.