Reducing Postharvest Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
131
4.8.
Summary of the Case Study Findings
For each of the seven case studies that focused on food crops, postharvest losses are complex
and differ by commodity and target markets. These are summarised in Table 60. While losses
in terms of physical and economic terms are reported, in practice they will substantially vary
even for the same commodity because value chains can be quite different. There is no single
measure that will reduce postharvest losses due the vast array of products and uniqueness of
each market.
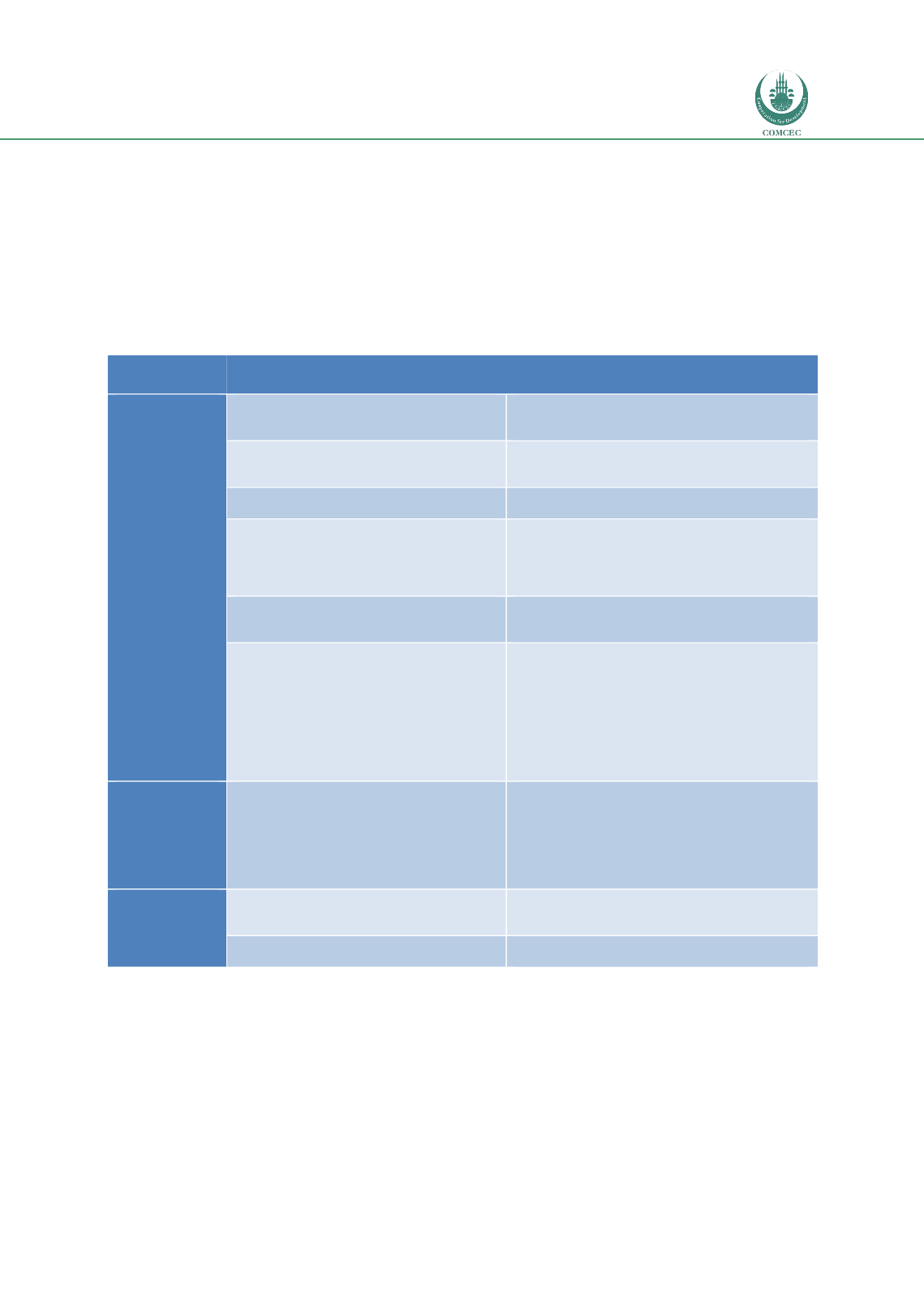
Table 60: Summary of causes and mitigation for the cases studies
Case /desk
study
Causes of postharvest losses
Means for reduction of postharvest
losses
Cereals in
Egypt
Late harvesting leading to infestation and
grain left in the field
Awareness of optimal harvest timing, field
infestation risk. Better advanced planning for PH
activities
Drying in the field
Stooking and/or quick removal of mature crop from
field. Use of clean sheets/ containers to protect crop
Transport management
Better advanced planning & monitoring of PH
activities
Inadequate threshing and shelling
Erect sides around threshing/shelling platforms and
sheets underneath, gentler beating to prevent
breakage, timely harvesting before crop over
matures, maintenance/ knowledge of threshing
machine to minimise breakage
Suboptimal Sorting
Awareness: removing broken grains reduce pest
damage. Support development of quality sensitive
markets
Suboptimal Marketing
Farmer organisation share transport, market info,
increase access to credit and negotiation positions.
Support development of quality sensitive markets,
enforce grain standards efficiently and equitably.
More efficient payment systems (e.g. mobile money).
More efficient less complex grain import systems.
As private sector procurement of domestic grain
increases, warehouse receipt systems may have a
role
Suboptimal Storage
Training on improved grain storage for farmers,
extensionists, teachers, traders/importers and store
managers. Thorough cleaning and maintenance of
stores. Better protection of grain to be stored (e.g.
use of hermetics, recommended pesticide
application for farmers; fumigation, rodent mgmt. &
hygiene of large stores)
Suboptimal Milling
Increased training in mill hygiene, product
separation, rodent proofing and preventative
maintenance. Monitoring and investment.
Suboptimal Utilisation
Awareness raising on food safety issues and food
choices