Increasing the Resilience of the Food Systems
In Islamic States in Face of Future Food Crises
129
5.2.
Survey Feedback
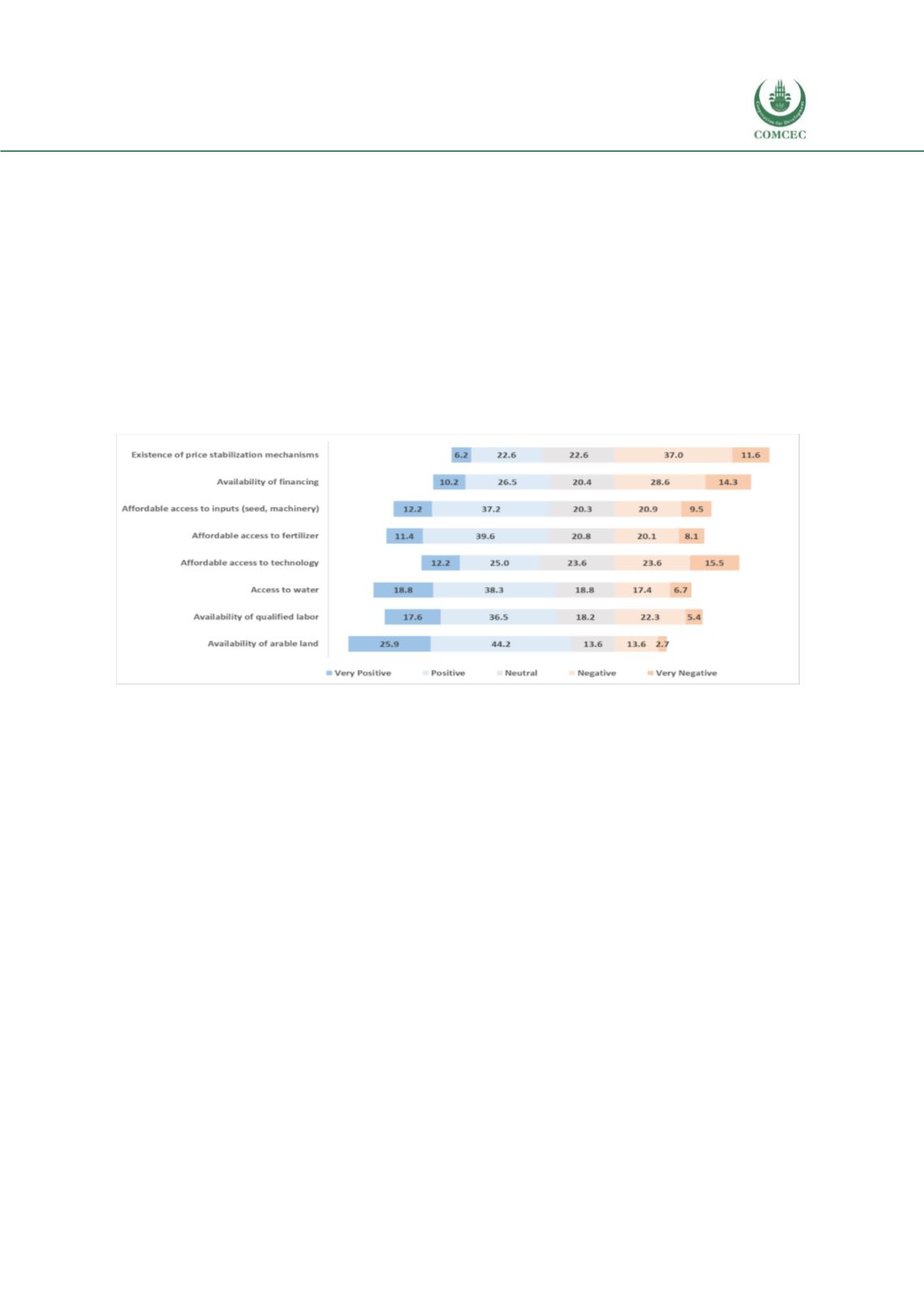
Respondents were asked to rate the role played by a number of support factors in enabling
agricultural production (including all categories, spanning grains, crops, meat, dairy, sugars) in
their countries. A five-point scale was used, including very positive, positive, neutral, negative,
and very negative. As the following chart illustrates the availability of arable land hadthe highest
positive rating (70%), followed by access to water (57%), availability of qualified labor (54%),
affordable access to fertilizers (51%), and affordable access to inputs including seed and
machinery (49%). Almost half of the respondents (49%) assigned a negative rating the existence
of the price stabilizationmechanisms, whichwas followed by availability of financing and access
to technology with a negative rating of 43% and 40% respectively.
Figure 32: Survey Findings - Rating of Factors Enabling Agricultural Production
Respondents were also asked in a related question on the ease with which farmers and
agricultural businesses in their countries are able to generate a reliable, sustainable living that
can support their families’ needs through growing a diversity of crops. A half of the respondents
(51%) believed that this is difficult for farmers, and only a third of the respondents (32%) cited
that it was an easy task while the remaining respondents were neutral.
Respondentswere asked torate the role played by a number of post-harvest factors in ensuring
that agricultural production is financially viable. A five-point scale was used, including very
positive, positive, neutral, negative, and very negative. As the following chart illustrates the
availability of sizable domestic end market had the highest positive rating (62%), followed by a
developed agro-industry (51%), good effective grain storage facilities and access to export
markets (50% each), and cost-effective and efficient transportation and logistics (48%).