Increasing the Resilience of the Food Systems
In Islamic States in Face of Future Food Crises
121
TheMinistry of Agriculture and Fisheries provides training and awareness programs to farmers.
In a bid to protect farmers’ interests, the Capital Market Authority in Oman launched an
insurance policy for the agricultural sector in 2017, to cover farmer associated risks and
maintain healthy levels of agricultural production.
493
The Ministry of Agriculture and Fisheries is also encouraging youth in Oman to commen ce
integrated farm projects by providing them land and intensive training programs. To enhance
food security, Omani locals are also given logistics and marketing support.
In response to the 2008 global food price crisis, the government implemented a food subsidy
system that was in place when food prices surged again in 2011.
494
In 2012-13, PASFRwith the
Public Authority for Consumer Protection (PACP) placed price caps on basic food items and
consumer goods for food security purposes.
495
Building Resilience: Future planning
To establish a resilient food system, the government set up Oman Food Investment Holding
Company (OFIC), a state-owned entity todevelop food related projects. OFIC has been pivotal in
creating alliances with key stakeholders offering guidance while identifying new investment
opportunities
496
.
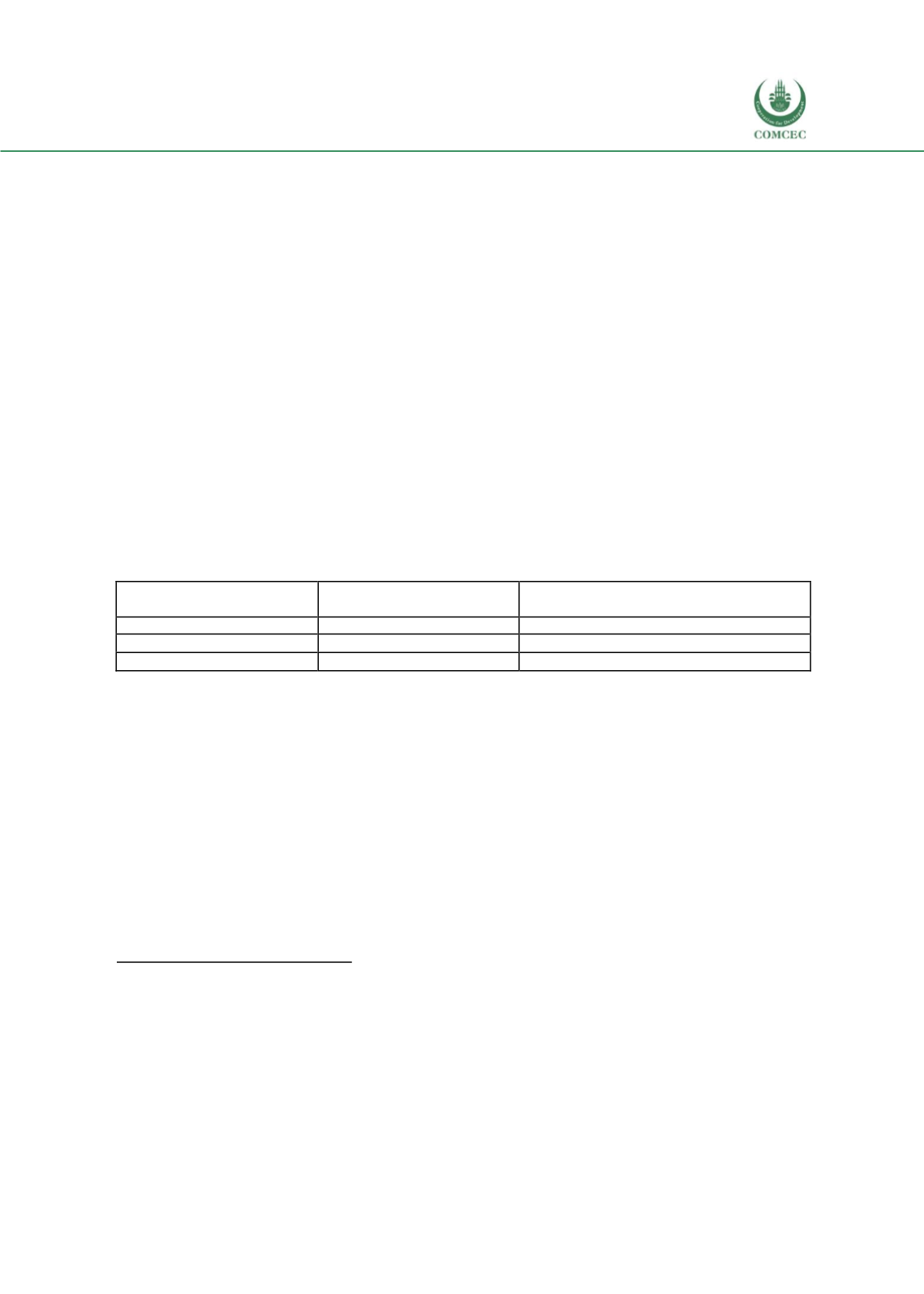
Table 63: Projects undertaken by Oman Food Investment Holding Company
Company
Capital Outlay
(Omani Rials, million)
Product
A’Namaa Poultry Co.
100
Poultry
Mazoon Dairy Co.
100
Dairy
Al Bashayer Meat Co.
37
Red Meat and livestock
Source: Oman Food Investment Holding Company
Oman had an agricultural research intensity ratio(investment in agricultural research as a
share of agricultural GDP) of 6.5%, in 2012, one of the highest worldwide. Oman’s intensity
ratio was much higher than other OIC countries in 2012 such as 1.84%in Jordan, 0.95% in
Lebanon, and 0.56% in Yemen
497
.
Oman has four agricultural research agencies, of which DGALR (Directorate General of
Agriculture and Livestock Research) is the largest, running six research centres specialized in
plant production and protection, soil andwater, livestock, and animal health. DGFR (Directorate
General of Fisheries Research) is Oman’s primary fisheries research directorate, consisting of
theMarine Science and Fisheries Centre, the Fisheries Quality Control Research Centre, and the
Aquaculture Research Centre
498
.
493
“Agriculture insurance policy in Oman to be extended to fishery sector”. Timesof Oman, 2018.
https://timesofoman.com/article/120080/Business/Economy/Agricultural-insurance-policy-in-Oman-to-be-extended-to-livestock-fishery-sector
494
“Food and water security to 2025 in Oman”. Future Directions, 2018.
http://www.futuredirections.org.au/publication/the-sultanate-of-oman-food-and-water-security-to-2025/495
Oman: Doing Business, Investing in Oman Guide Volume 1
496
Growing green strategic investments to boostself-sufficiency and exports”. Oxford Business Group, 2018.
https://oxfordbusinessgroup.com/overview/growing-green-strategic-investments-promising-sector-boost-self-sufficiency-and-exports
497
CGIAR website.
https://www.asti.cgiar.org/pdf/factsheets/Oman-Factsheet.pdf498
Ibid.