Reducing On-Farm Food Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
99
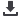
Possible Causes of Food Losses for Roots and
Tuber Crops
Arab Group
N = 18 (%)
Asian Group
N = 21 (%)
African Group
N = 16 (%)
Mechanical damage during postharvest handling
(rough handling, throwing, dropping)
13 (72.22)
13 (61.9)
11 (68.75)
Poor quality field containers or shipping
packages
14 (77.78)
14 (66.67)
10 (62.5)
Other Causes
Poor temperature management (too cold, too
hot, no cold chain)
13 (72.22)
11 (52.38)
13 (81.25)
Lack of proper storage facilities
14 (77.78)
13 (61.9)
14 (87.5)
Lack of proper food processing and packaging
14 (77.78)
12 (57.14)
11 68.75
Delays in transport/distribution
11 (61.11)
11 (52.38)
10 (62.5)
Poor roads and related infrastructure
12 (66.67)
10 (47.62)
10 (62.5)
Lack of marketing options
14 (77.78)
11 (52.38)
10 (62.5)
Consumption (waste)
9 (50)
6 (28.71)
10 (62.5)
Source: Key Informant Surveys.
4.1.3. Oilseeds and Pulses
Key informants in the Arab, Asian and African Groups indicated that many of the potential on-
farm causes of losses were important for their countries. The majority of the key informants in
the Arab Group identified poor planning, poor quality seeds, pests on the farm, poor cultural
practices, poor water management and plant diseases as the most important causes of food
losses for oilseeds and pulses. Key informants for Asian Group countries identifiedmany of these
same causes, and key informants for countries in the African Group identified these causes plus
mechanical damage and spillage on the farm.
Regarding other causes of losses, the majority of key informants in the Arab Group reported all
the possible causes including poor temperature management, lack of proper storage facilities,
processing, packaging, infrastructure, and marketing options. A key informant from UAE
reported “decoration waste” as a cause of oilseeds and pulses losses. For the Asian Group, only
lack of processing and packaging was viewed as an important cause of losses, and for the African
Group, key informants identified lack of storage and lack of processing and packaging. One key
informant in Turkey reported on rancidity problems and oxidation as an important cause of
oilseeds losses.
For less perishable crops like oilseeds and pulses, these are commonly found causes of losses.
Very few of the key informants mentioned delays in transport or temperature management as
problems.