Reducing On-Farm Food Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
104
Watering: readymade waterers or improvised;
Housing: type of housing and night shelter;
Identification of poor growth or weak chicks and their management;
Regular vaccination: for which diseases and when;
Control of mortality: reasons for mortality such as disease, predator attacks or poor
management;
Post mortem of dead birds for proper diagnosis and control: whether to take the dead
birds for post mortem or not, and if yes, where and how to get it done;
Weighing the birds at different stages: how to weigh and approximate required weights
at different ages;
Recording of feed consumption and egg production.
Poultry farmers therefore need different types of advice and also the knowledge and skills to
improve their on-farm practices (Sasidhar 2009).
4.1.5. Milk and Dairy
Key informants in the Arab, Asian and African Groups indicated that animal diseases were the
most important of on-farm causes of losses for milk and dairy. In addition, for the Asian Group,
the majority of key informants identified poor information and planning as an important cause
of on-farm losses.
Regarding other possible causes, key informants in all three OIC Member Country Groups
included poor temperature management, lack of proper storage, processing and packaging,
transport, infrastructure, and marketing options. These are all commonly found causes of losses
for perishable foods. In addition, one key informant in Gabon reported on the “lack of
laboratories for assessing quality and safety” and for the UAE an important cause of losses for
milk and dairy products is “decorative waste.”
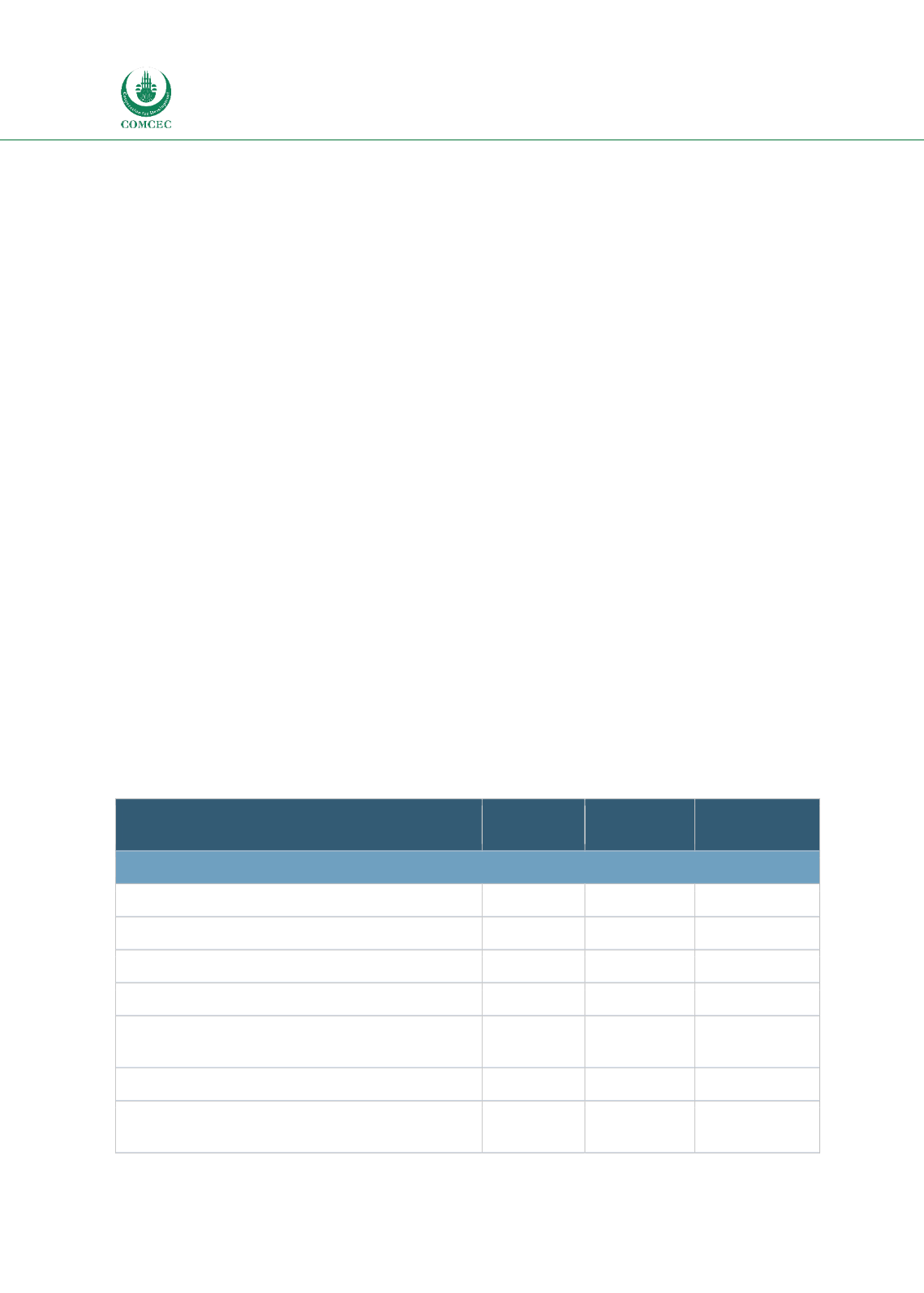
Table 4.7: Tally of Numbers and % of Key Informant Responses for Milk and Dairy
Possible Causes of Food Losses for Milk and
Dairy
Arab Group
N = 19 (%)
Asian Group
N = 24 (%)
African Group
N = 18 (%)
Pre-Harvest Causes
Poor information and planning
7 (53.85)
12 (60)
6 (42.86)
Lack of inputs (feed, etc.)
3 (23.08)
4 (20)
5 (35.71)
Poor quality starting materials
1 (7.69)
0
1 (7.14)
Pests on the farm (weeds, insects, rodents)
4 (30.77)
4 (20)
3 (23.08)
Poor cultural practices (pruning, fertilizing,
Pesticide spraying)
2 (15.38)
1 (5)
2 (14.29)
Poor water management or drought
4 (30.77)
4 (20)
1 (7.14)
Animal diseases on the farm (fungi, viruses,
bacterial rots)
9 (69.23)
7 (35)
9 (64.29)