Reducing On-Farm Food Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
105
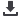
Possible Causes of Food Losses for Milk and
Dairy
Arab Group
N = 19 (%)
Asian Group
N = 24 (%)
African Group
N = 18 (%)
Harvesting Causes
Poor harvesting practices (damaged by cuts,
bruises, etc.)
5 (38.46)
5 (25)
3 (23.08)
Wrong time for harvest (immature, over-mature)
1 (7.69)
0
0
Mechanical damage during postharvest handling
(rough handling, throwing, dropping)
1 (7.69)
3 (15)
3 (23.08)
Poor quality field containers or shipping packages 4 (30.77)
9 (45)
5 (35.71)
Other Causes
Poor temperature management (too cold, too hot,
no cold chain)
11 (84.62)
16 (80)
10 (71.43)
Lack of proper storage facilities
10 (76.92)
17 (85)
13 (92.86)
Lack of proper food processing and packaging
9 (69.23)
13 (65)
9 (64.29)
Delays in transport/distribution
10 (76.92)
10 (50)
10 (76.92)
Poor roads and related infrastructure
8 (61.54)
11 (55)
9 (64.29)
Lack of marketing options
11 (84.62)
10 (50)
7 (50)
Consumption (waste)
9 (69.23)
5 (25)
7 (50)
Source: Key Informant Surveys.
4.1.6. Fish and Seafood
Key informants in the Arab, Asian and African Groups indicated that poor information and
planning and poor quality field containers or shipping packages were the most important causes
of on-farm losses for fish and seafood.
Regarding other possible causes of losses, the majority of key informants in all three OIC
Member Country Groups included poor temperature management, lack of proper storage,
processing and packaging, transport, infrastructure, and marketing options. These are all
commonly found causes of losses for perishable foods. In addition, one key informant in Burkina
Faso reported on the “unhygienic conditions” and for the UAE an important cause of losses for
fish and seafood products is “decorative waste.”