Promoting Agricultural Value Chains
In the OIC Member Countries
41
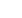
Figure 3-9 Top Six livestock and agriculture produce in value in the OIC, 2004-2006
Source: FAOSTAT, 2015
For palm oil and rice, OIC Member Countries were also among the top 5 producers worldwide:
Malaysia, Indonesia and Nigeria for palm oil, and Indonesia and Bangladesh for rice
. Table 3-1below shows that individual OIC Member Countries were leading only in relatively few highly
traded commodities from 1993-2013. These include, next to the already mentioned palm oil
and rice, coffee, cocoa, cotton, tea and sugarcane. Most products which see a leading position of
individual OIC countries include minor cereals (millet and sorghum), minor fruits (dates and
figs), spices (pepper and vanilla), minor roots and tubers (sweet potato and yams) as well as
minor legumes (cow peas).
The position as top producing country does not indicate that these countries are also leading in
terms of yields in the respective product. For instance, cocoa production sees Cote d’Ivoire,
Indonesia and Nigeria on positions 1, 2 and 4 worldwide. However, none of them appear in the
list of countries with the highest cocoa yields. The only OIC country to make an appearance is
Malaysia as the country with the worldwide 5th highest yields. This may have to do with use of
fertiliser and level of mechanisation in the OIC, which are both lower than the world average.
Generally poor ecological conditions for agriculture, such as limited water sources and climatic
conditions, may also contribute to the relatively low yields in OIC countries.
0
5000
10000
15000
20000
25000
30000
35000
Rice, paddy Milk, whole fresh
cow
Yams
Wheat
Chicken meat
Oil, palm
Million US$