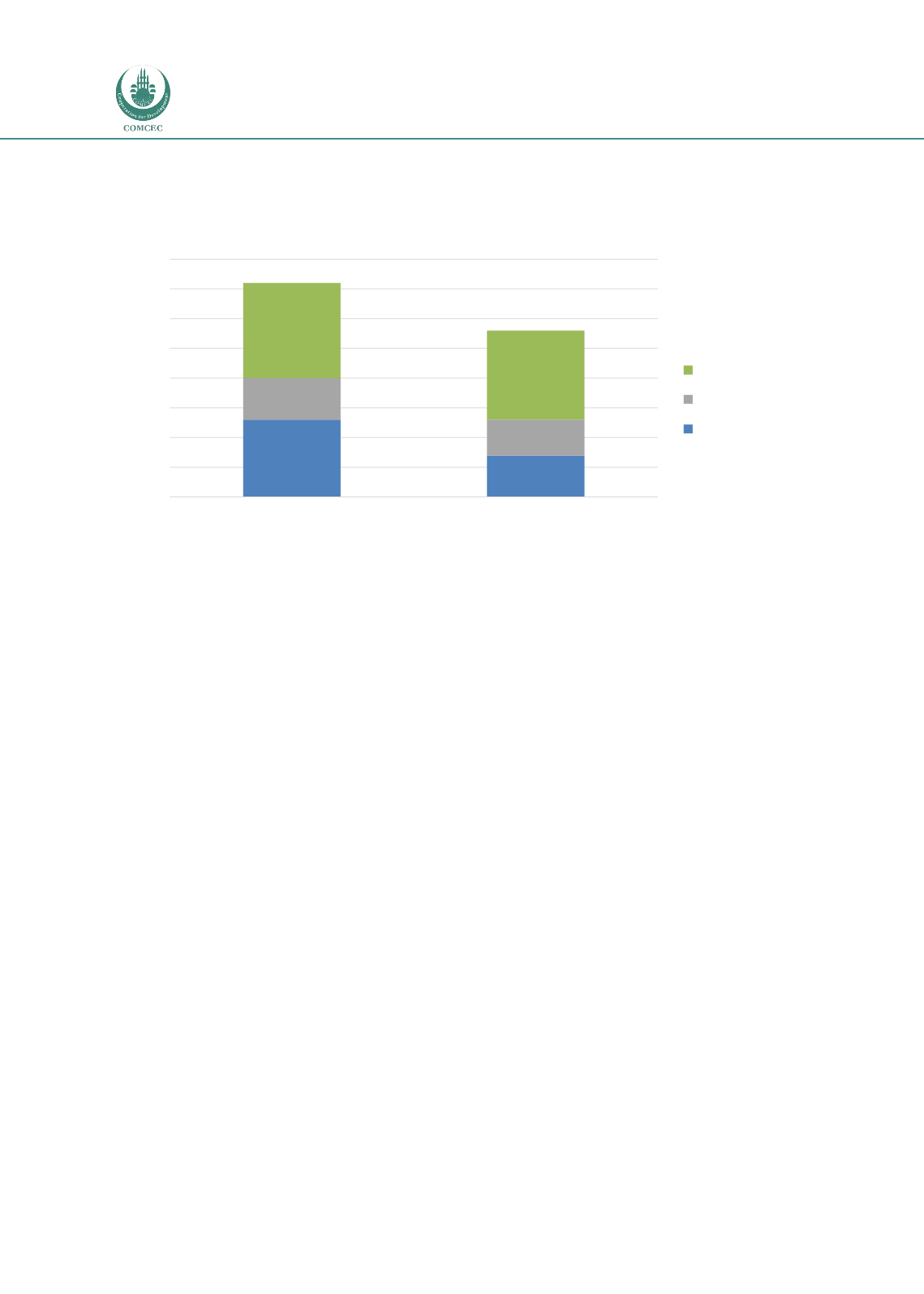
Promoting Agricultural Value Chains:
In the OIC Member Countries
36
reliable and up-to-date data, market performance and access as the output areas. An important
way to achieve these outputs is by developing agricultural value chains.
Figure 3-2 Agricultural importance of the OIC, 2013
Source: WDI, 2015
In many OIC Member Countries, agriculture is an important sector, both as a contributor to
GDP and as a source of employment. As regards the former, agriculture accounted for 9
percent of GDP in 2013 in the OIC (see Figure 3-3), while manufacturing had a share of 12
percent, industry 37 percent and services 42 percent. Agriculture was responsible for 10-19
percent in 10 out of 57 OIC countries, 20-29 percent in 13 countries, 30-39 percent in 4
countries, and more than 40 percent also in 4 countries. In the latter four countries (Chad,
Guinea-Bissau, Mali and Sierra Leone), agriculture was also the most important sector in the
economy.
Agriculture and agribusiness together account for nearly half of GDP in Africa. Agricultural
production is the most important sector in most African countries, averaging 24 percent of
GDP for the region. Agribusiness input supply, processing, marketing, and retailing add about
20 percent of GDP (World Bank, 2013).
The role of agribusiness becomes more pronounced with rising incomes. Globally, agribusiness
is about 78 percent of value added in the agricultural value chain, with farming constituting
the remainder, although the share varies widely across countries and income levels. The ratio
of value added in agribusiness to that in farming is 0.6 in agriculture-based countries (most of
Africa), but the ratio increases to 2 for transforming countries (mostly Asia), 3.3 in urbanised
countries (mostly Latin America), and 13 in the United States (World Bank, 2013). The share of
upstream and downstream agribusiness in total GDP rises to as much as 30 percent in middle-
income countries, even as the share of primary agricultural production in the economy is
decreasing rapidly. These trends reflect the commercialisation of farming to meet rising
demand from urban consumers, leading to higher use of purchased inputs; increased services
for machinery repair, finance, and retail; and greater demand for processing, packaging, and
transportation (World Bank, 2013).
13%
7%
7%
6%
16%
15%
36 % (OIC total)
28 % (OIC total)
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
30%
35%
40%
Share of world's arable &
permanent crop land
Share of world's GDP
Asian Group
Arab Group
African Group