Reviewing Agricultural Trade Policies
To Promote Intra-OIC Agricultural Trade
65
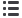
Exporter
Product
Share of the
product in
the
exporter’s
total agr.
exports, %
Share of the
country in
the total
world export
of the
product, %
Share of OIC
as destination
for the
country's
export of the
product, %
Weighted average
tariff rates
implemented by
OIC members to
the country's
export of the
product, %
Burkina
Faso
Sesame (Sesamum) seeds
4,2
1,4
23,0
1,4
Oil-seeds & oleaginous
fruits, n.e.s.
3,3
1,8
2,3
0,0
Source: ITC Macmap, CEPII BACI, Eurostat RAMON, UN Comtrade, UN Trade Statistics, and authors’ calculations.
Note: This table collects information on the global and OIC market shares of countries’ top export products at the product level
and weighted average tariff rates these products face at the OIC markets. Each column is colored according to the thresholds
indicated at the first row. To take just one example, “Other beet/cane sugar in solid form, other than flavoured/coloured matter”
from Algeria has a large share within Algeria’s agricultural exports (larger than 10%) as indicated in the colored third column.
This product is important, and hence the fourth column is colored, also because 0.9% of Algerian share in “Other beet/cane sugar
in solid form, other than flavoured/coloured matter” is larger than the overall Algerian share in agricultural products.
Furthermore, the share 98.7% of OIC markets for Algerian “Other beet/cane sugar in solid form, other than flavoured/coloured
matter” is larger than the overall OIC share of agricultural products from Algeria, and the fifth column is also colored. Finally, the
last column is colored for in “Other beet/cane sugar in solid form, other than flavoured/coloured matter” because the weighted
average applied tariff rates faced by this product by Algerian exporters in OIC markets is larger than the corresponding rates
applied to overall agricultural exports from Algeria in OIC markets.
A vast majority of participants states that agricultural trade is either very important (67%) or
important (21%) to the country’s overall agricultural development. Similar figures are observed
with regards to the role of agricultural trade on food security (72% and 22%, respectively). This
is expected given the large share of the agricultural sector in employment and GDP in OIC
member countries generally. But it also indicates that the design and implementation of sound
agricultural trade policies would result in significant positive effects on the social and economic
welfare in the OIC member countries.
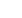
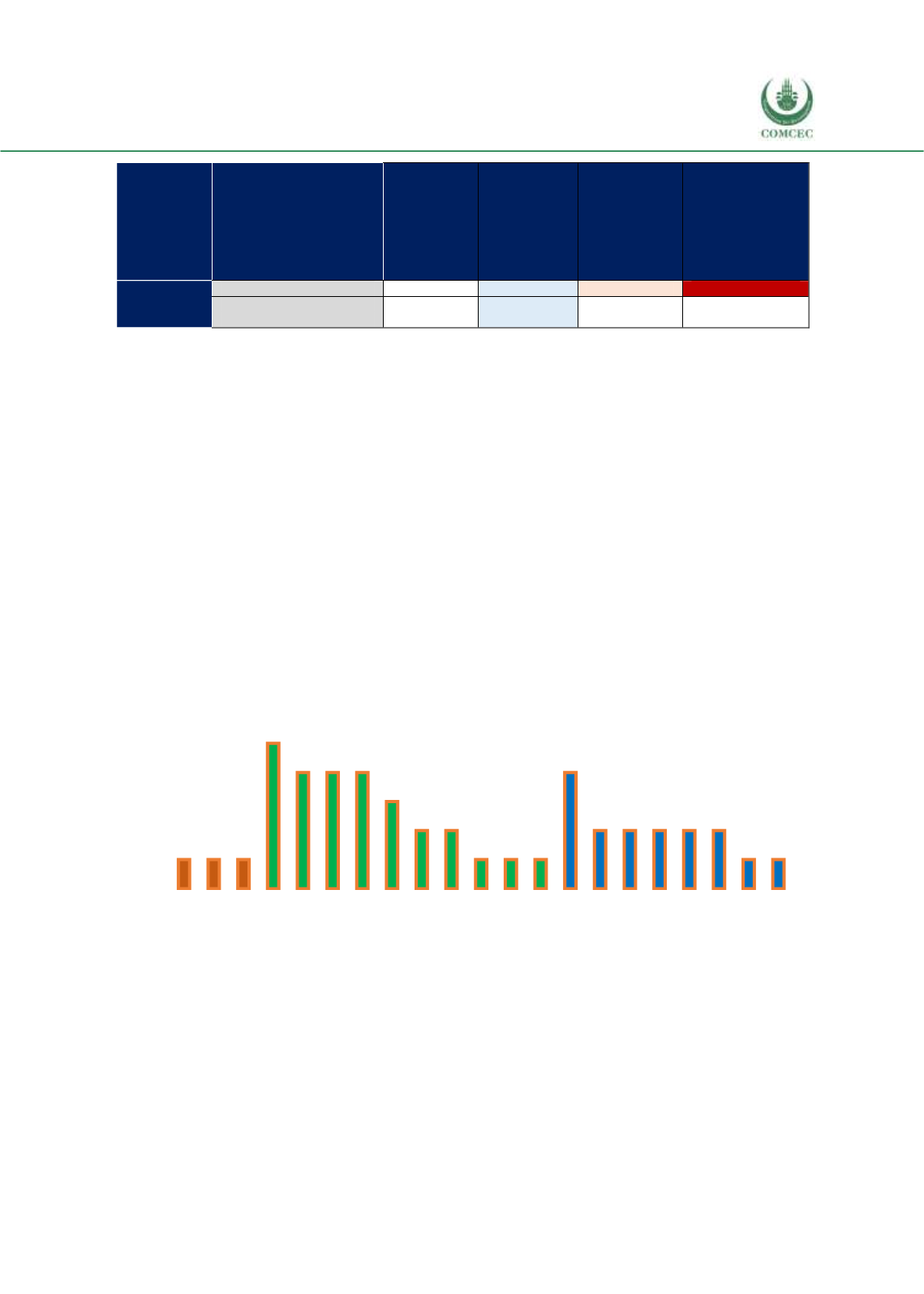
Figure 3. 15 Distribution of Survey Participants across Countries
Source: Authors.
0%
2%
4%
6%
8%
10%
12%
Cote d'Ivoire (1)
The Gambia (1)
Uganda (1)
Egypt (5)
Lebanon (4)
Palestine (4)
Tunisia (4)
Jordan (3)
Morocco (2)
Qatar (2)
Algeria (1)
Sudan (1)
United Arab Emirates…
Turkey (4)
Brunei-Darussalam (2)
Indonesia (2)
Iran (2)
Malaysia (2)
Pakistan (2)
Afghanistan (1)
Suriname (1)