92
b)
The
Takaful
model that was represented in the first insurance experience in the
Saudi Arabia was implemented by the National Cooperative Insurance Company; a
government insurance company established by a Royal Decree in 1985. This
Company was later renamed the Company for Cooperative Insurance). The
Takaful
model adopted by the Company was based on Mudarabah. It was managing the
insurance and investment funds of 25% of the proceeds from policyholders’
premiums. The
Takaful
was charging the actual administrative and management
expenses of the
Takaful
fund. The Takaful Company, however, was not able to meet
the profitability benchmark of feasibility study unlike the insurance companies
operating in the market in the kingdom.
c)
The cooperative model proposed by the Council of Senior Scholars in the Kingdom
in resolution No. 51 for the year 1395 AH was not practical because it required the
contribution by the insured (policyholder) to be a mere donation. This means that
the beneficiaries of the
Takaful
fund could include policyholders and others who do
not hold insurance policy or do not contribute to the fund. Furthermore, the surplus
from the insurance must be channelled to charity and the policyholders are not
entitled to benefit from such surplus because their donation is separate from their
liability.
d)
The cooperative model has been criticized by scholars from Saudi Arabia due to its
inherent
Shari’ah
issues. Fatwas critical of the cooperative model include those
issued by the S
hari’ah
advisory board of Al-Ahli Bank no. 89.
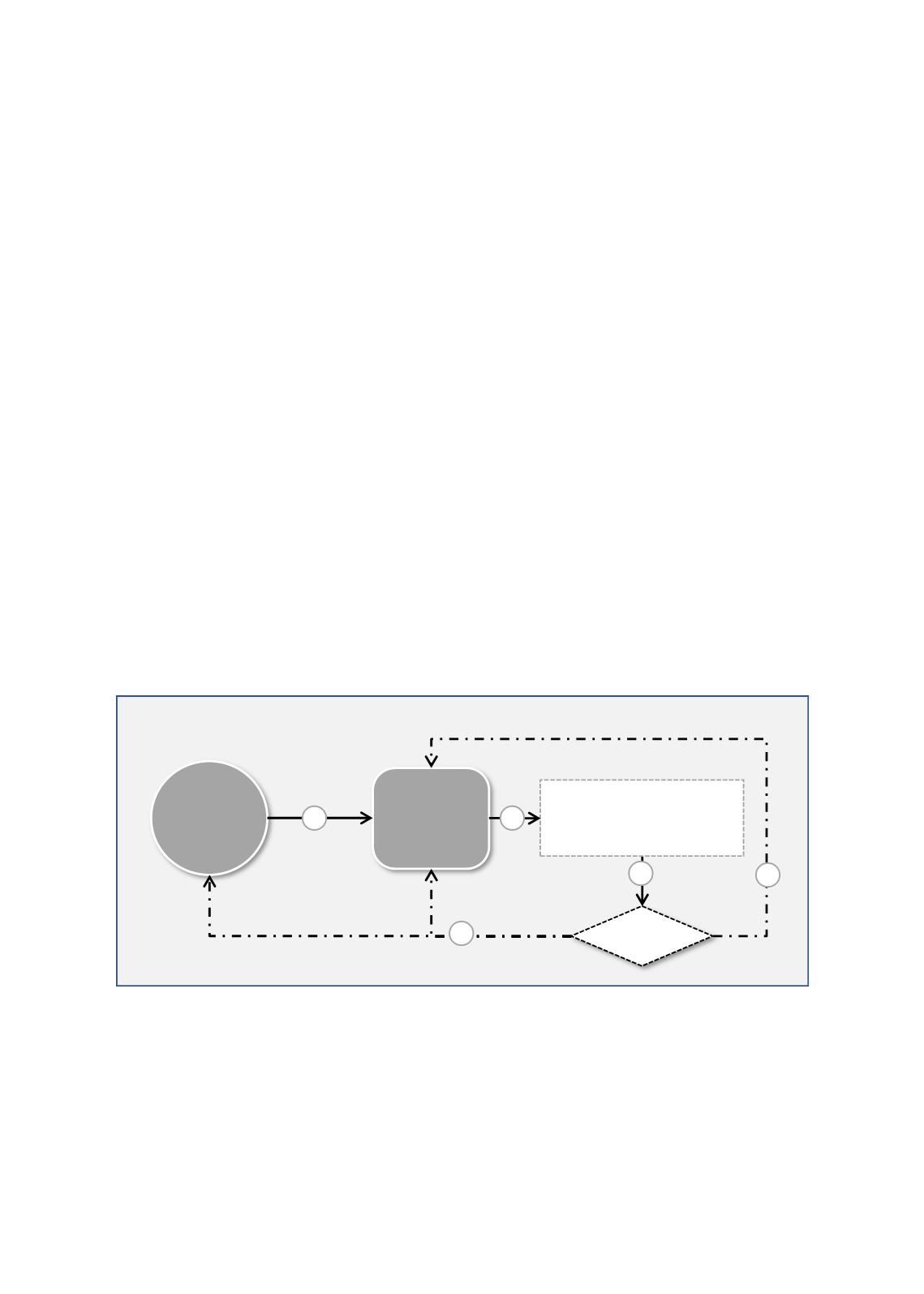
F
IGURE
18: T
HE
F
LOW CHART OF THE
1
ST
C
OOPERATIVE
I
NSURANCE
M
ODEL IN
S
AUDI
A
RABIA
Source: Cooperative Insurance Companies Control Law 2004, Interview with Sulaiman Mohammed Aljewisser
Description/ illustration of the Model:
Figure 18presents the standard model implemented by the insurance companies in Saudi
Arabia, where:
TPs
TO
Surplus
?
Contribution
Yes
No
10%
90%
•
Operating Expenses
•
Investment Outcome
•
Claims
1
2
3
4
5