147
capital, risk governance, and transparency and disclosure are in place to ensure stability and
sustainability of the financial institutions including TOs. In addition, there are also prudential
standards and requirements which specifically cater to distinct features of Islamic finance.
These standards strengthen the governance of TOs, provide greater clarity on the use of multiple
Shari'ah
contracts in the models and structures of
Takaful
, and safeguard the interests of
Takaful
participants.
In general, the
Takaful
industry lacks a comprehensive legal and regulatory framework. The
major challenges include lack of
Takaful
Act, specific laws and standardization of financial
accounting and reporting, and tax laws related to
Takaful
. For example, in Turkey there is no
specific
Takaful
act. The banking sector in the country is mainly regulated by BRSA and CMB. In
contrast, Malaysia has
Takaful
regulatory framework in place pending specific laws.
8.2.
Shari'ah
Framework
All the activities of
Takaful
must be guided by the
Shari'ah
. Apparently, there is a variation to the
degree of
Shari'ah
framework for
Takaful
in the four countries selected for this study: Saudi
Arabia, Malaysia, Turkey and UK. Among all the four countries, Malaysia has made tremendous
progress in terms of
Shari'ah
framework for
Takaful
. Its Islamic Financial Service Act (IFSA,
2013) provides a comprehensive
Shari'ah
framework that recognizes the specificities of
Takaful
.
T
ABLE
23:
S
HARI
'
AH
I
SSUES AND
P
OLICY
R
ECOMMENDATIONS
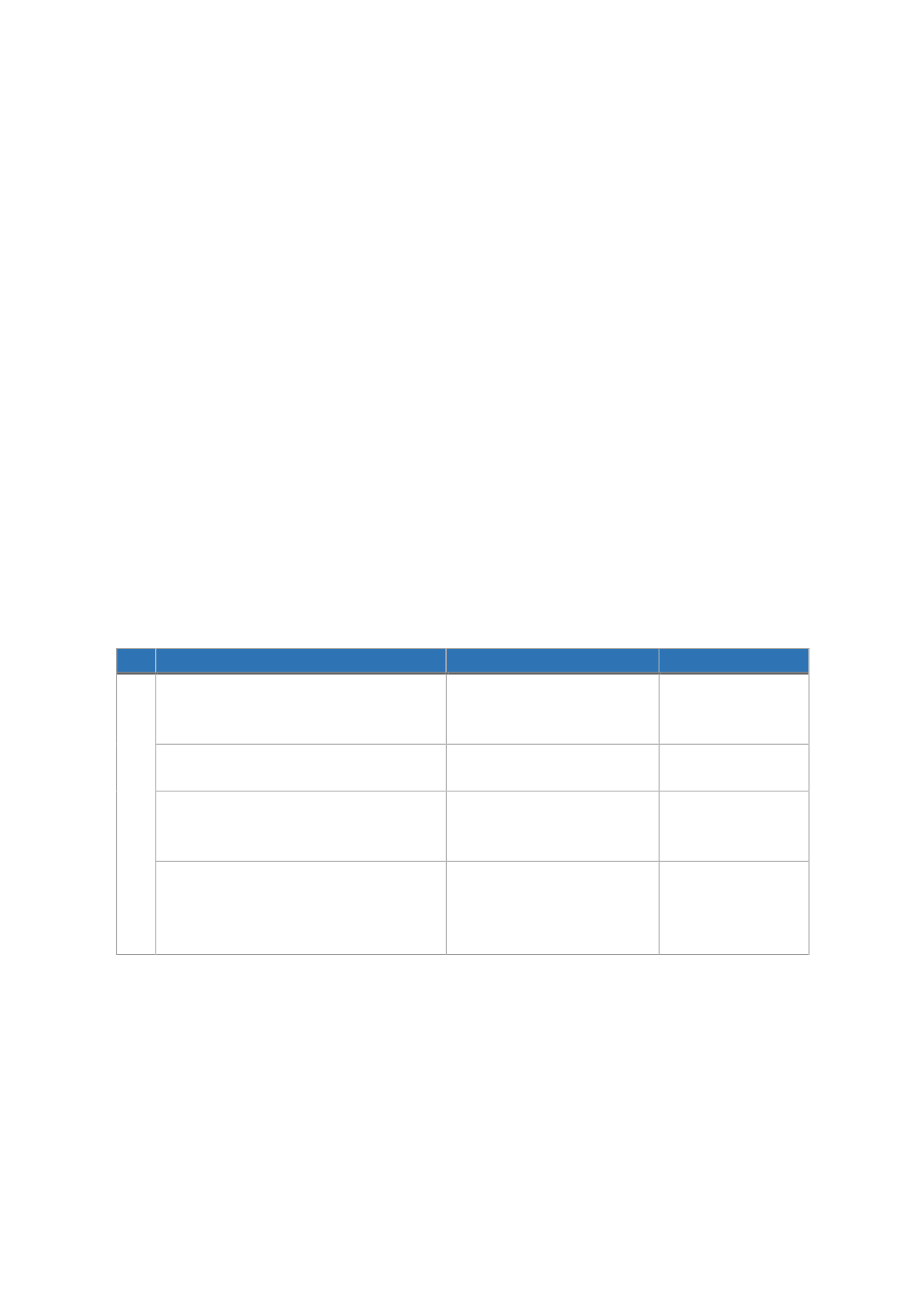
No
Issues
Policy Recommendation
Country Affected
2
2.1. Absence of a comprehensive
Shari'ah
governance framework
for
Takaful
Developing a
Shari'ah
governance framework
for
Takaful
UK, Turkey and
Saudi Arabia
2.2. Lack of
Takaful Shari'ah
standards
Developing
Takaful
Shari'ah
standards
UK, Turkey and
Saudi Arabia
2.3. Conflict between the existing
legal framework and
Shari'ah
requirements
Harmonizing the existing
legal framework with
Shari'ah
requirements
Applies to all the
four countries
2.4. Absence of
Shari'ah
conflict
resolutions
Establishing
Shari'ah
units
for conflict resolutions
and empowering
Shari'ah
committees
UK, Turkey and
Saudi Arabia
Source: Authors
The
Shari'ah
Advisory Council (SAC) as part of the
Shari'ah
governance framework is the apex
authority that guides the
Takaful
industry on
Shari'ah
related issues. IFSA has also paved the
way for the development of various
Shari'ah
standards to guide TOs. These standards
strengthen the governance of TOs, provide greater clarity on the use of multiple
Shari'ah
contracts in the models and structures of
Takaful
, and safeguard the interests of
Takaful
participants. In the other three jurisdictions, Turkey, Saudi Arabia and the UK, there is the
absence of Islamic finance and
Takaful
act and lack of central
Shari'ah
board.
The insurance