
Improving Public Debt Management
In the OIC Member Countries
73
Debt management strategy (incl. risk management)
The objectives of the debt management strategy of Gambia, which are highlighted in the Public
Finance Law, are primarily to ensure that the government meets its financing needs and
payment obligations at the lowest possible costs over the mediumto longterm with a
prudent degree of risk. The debt management strategy also promotes the development of the
domestic debt market. The MoFEA created the first MTDS for the years 20102012 (MoFEA
2012). The 20102012 strategy aimed at maximizing domestic borrowing and significantly
reducing external borrowing. External debt should mainly come from multilateral and bilateral
concessional sources with a grant element of at least 35%.
Domestic debt increased over the period 2010 to 2012 because of the issuance of (shortterm)
TBills. The domestic debt portfolio was thus prone to high interest and refinancing risks.
Consequently, the MTDS of 20112014 focused on addressing the challenges of the domestic
debt portfolio. The key aims of the MTDS 20112014 were to target NDB at 0.9% of GDP at the
end of 2014, to reduce domestic borrowing and to lengthen the maturity profile of the
domestic debt by introducing three year nominal bonds and – in the medium term five year
bonds (MoFEA 2014). The implementation of the MTDS 20112014 was difficult due to fiscal
dominance and an underdeveloped domestic debt market. Heavy domestic borrowing
requirements gave rise to increasing interest rates and higher refinancing risks because of
high costs of lengthening maturities (see also Table 41).
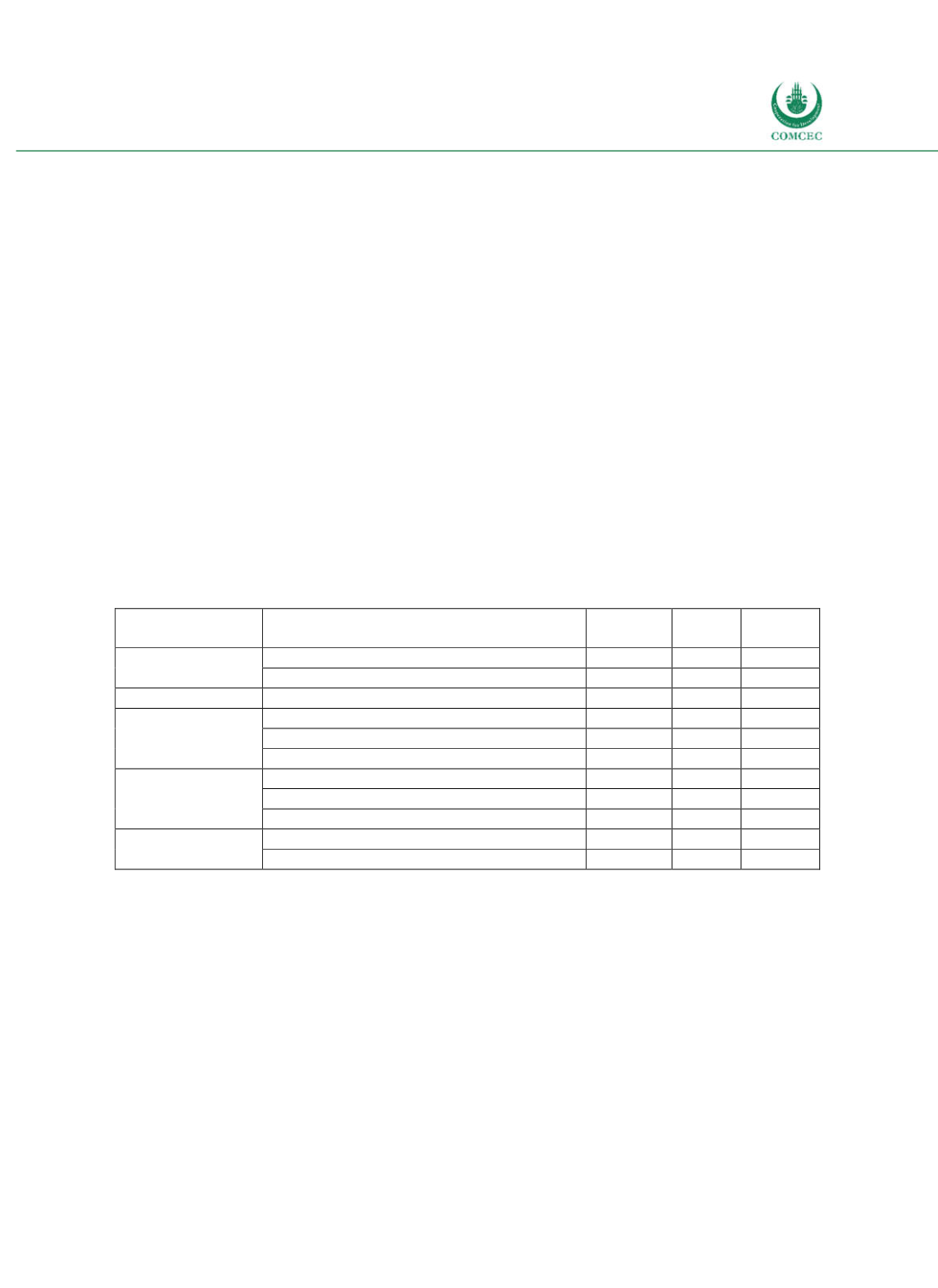
Table 4-1: Gambia – Cost and Risk Indicators for the Government's Debt Portfolio (2014)
Type of risk
Risk indicator
2010
Baseline
2014
Actual
2014
Targets
Solvency
Nominal debt as % of GDP
68.3 105.0 59.8
PV of debt as % of GDP
57.5
90.0 46.1
Cost of debt
Implied interest rate
5.3
6.0
5.2
Refinancing risk
ATM external portfolio (years)
13
11.1 15.4
ATM domestic portfolio (years)
3.8
2.6
4.6
ATM total portfolio (years)
9.1
7.5
12.6
Interest rate risk
ATR (years)
9.1
7.3
12.6
Debt refixing in 1 year (% of total)
34.2
40
15.4
Fixed rate debt (% of total)
100.0 97.1 100.0
Exchange rate
risk
FX debt (% of total)
57.0
57.9 72.7
ST FX debt (% of total)
8.9
15.7
8.4
Note: ATM = Average Time to Maturity; ATR = Average Time to Refixing; FX = Foreign exchange; ST = Short-term.
Source: MoFEA (2014).
The objectives of the MTDS 20152017 are to reduce public debt by decreasing NDB towards
1% of GDP and to increase external borrowings in particular from the concessional window
(MoFEA 2015). Based on three different shock scenarios, the risks of four different debt
management strategies are evaluated in the MTDS. The favored strategy envisions a
progressive reduction of the NDB to 2% of GDP in 2015, 1% of GDP in 2016 and zero
thereafter (MoFEA 2015). Domestic borrowing is financed at 100% by TBills and external
borrowing is a mixture of semiand concessional external borrowing. The MTDS 20152017
further discourages central bank financing as it creates inflationary pressure (MoFEA 2015).
















