
Risk Management in
Islamic Financial Instruments
15
instruments that avoid interest, but are not profit sharing, i.e.
mudaraba
, which is the Islamic
contract that is most frequently engaged in (Greuning and Iqbal, 2008).
Islamic financial contracts vary in function, scope, and complexity. Thus, it is important that
the reader understands the profile of contracts within the Islamic financial system. Please find
an outline of the various Islamic financial contracts relevant to our discussion, largely derived
from Hawary, Grais and Iqbal (2003).
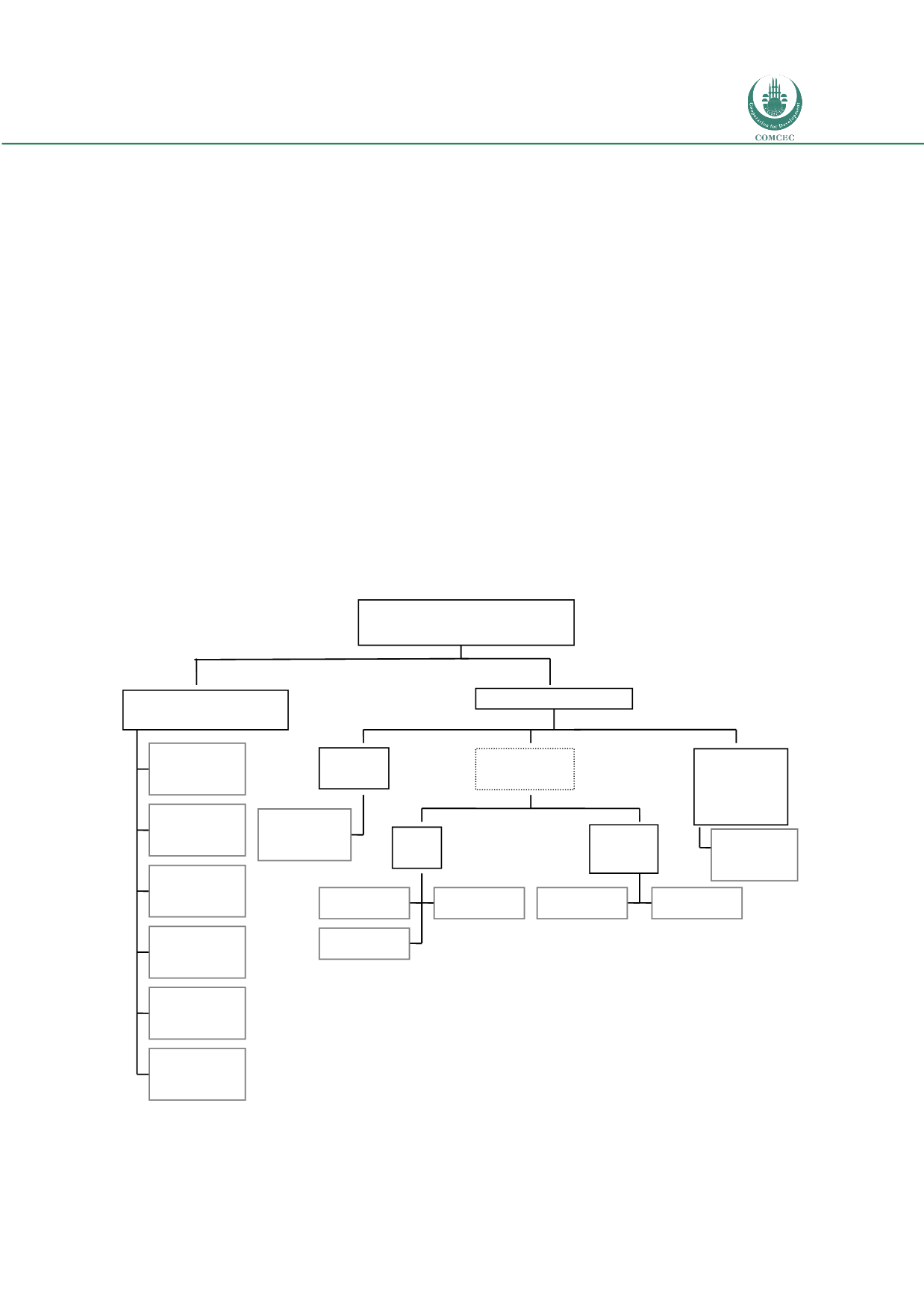
2.2 ISLAMIC FINANCIAL CONTRACTS
For the purposes of efficacious comprehensibility, it is useful to divide the contacts into three
categories: (1) Intermediation contracts:
Mudaraba, Amana, Takaful, Kifala, Joala, Wakala
; (2)
Transaction Contracts:
Qard Hasana
; and (3) Asset-Based contracts: a. Trade Financing
(
Murabaha, Baimuajjal, bai salaam
) b. Collateral-based (
Ijara, Istisna
) c. Equity Based:
Musaharaka.
Please see Figure 2.1, which was adapted from World Bank presentation
materials from the International Conference on Islamic Banking: Risk Management,
Regulation, and Supervision (2003).
Figure 2.1 Islamic Financial System (IFS)
Mudarabah
Kifala /Aqd-Daman
Ammanah
Takaful
Wikalah
Joala
Intermediation Contracts
Qard
Hassanah
Miscelleneous
Murabaha
Bay Mua'ajal
Bay salam
Trade
Financing
Ijarah
Istisna
Collateralised
Securities
Asset
Based
Securities
Musharaka
Equity
Participation
Transactional
Contracts
Profile of Contracts

















