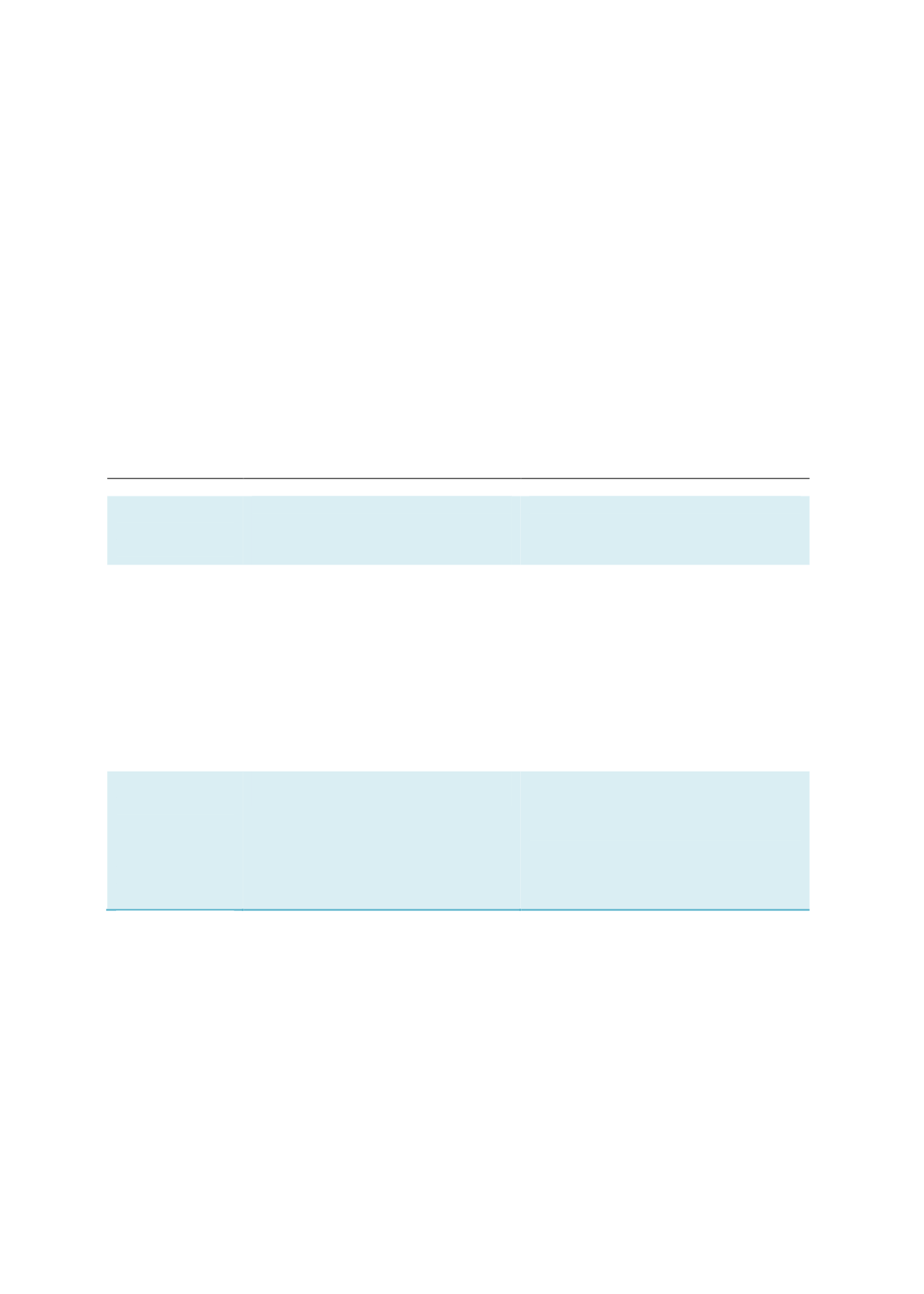
190
6.
CONCLUSION
This final section summarises the key findings and recommendations of the study, which can
be categorised into 3 main dimensions:
Sukuk structures
Sukuk issuances (supply – sell side)
Sukuk investments (demand – buy side)
These 3 dimensions have been used to measure the development of sukuk markets in the case
studies and assess the main challenges faced by the particular country. Central to the
development of a sukuk market is having a comprehensive framework that emphasizes 3 key
components, as exemplified in Table 6.1.
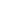
Table 6.1: Key Components of a Comprehensive Framework to Develop a Sukuk Market
Component
Role
Responsible Stakeholder
Legal and
regulatory
framework
To improve the existing legal, regulatory,
Shariah governance and tax frameworks
to level the playing field between sukuk
and conventional bonds.
Ministry of Finance (or its equivalent)
Capital-market authority
Tax authority
National Shariah authority
Market and
infrastructure
development
To develop an active Islamic money
market to support secondary trading, an
electronic trading platform for
transparency and to monitor issuances
and for price guidance.
Central bank
Securities and commodities
exchanges
To promote the issuance of LCY and FCY
sukuk that have different commercial
features (i.e. tax neutrality and
incentives, competitive costs, innovative
structures catering to various needs, and
benchmark yield curves) to attract
market players to tap the sukuk market.
Ministry of Finance (or its equivalent)
Tax authority
Central bank
Government-related entities
(GREs)or their equivalent (i.e.
SOEs/GLCs)
Corporate Issuers
Diversified
market players
on the supply
and demand
sides
To foster supply (sell side) of and
demand (buy side) for sukuk issuance.
Government
Service providers (investment banks,
securities companies, advisory
houses, brokers, traders, rating
agencies)
Banking institutions and their
holding companies
NBFIs
Sources: RAM, ISRA
The study shows that countries with an active LCY bond market spearheaded by corporates
make it easier to promote sukuk as an alternative form of financing. The following sub-sections
summarise the current status of the different sukuk markets based on the abovementioned
aspects.
6.1
SUKUK STRUCTURES
AAOIFI Shariah Standard No. 17 on Investment Sukuk has paved the way for the issuance of
various sukuk structures, particularly in Arab countries. While
ijarah
contracts constitute a
large portion of sukuk issuance in that region, recent trends indicate that
wakalah/wakalah bil