187
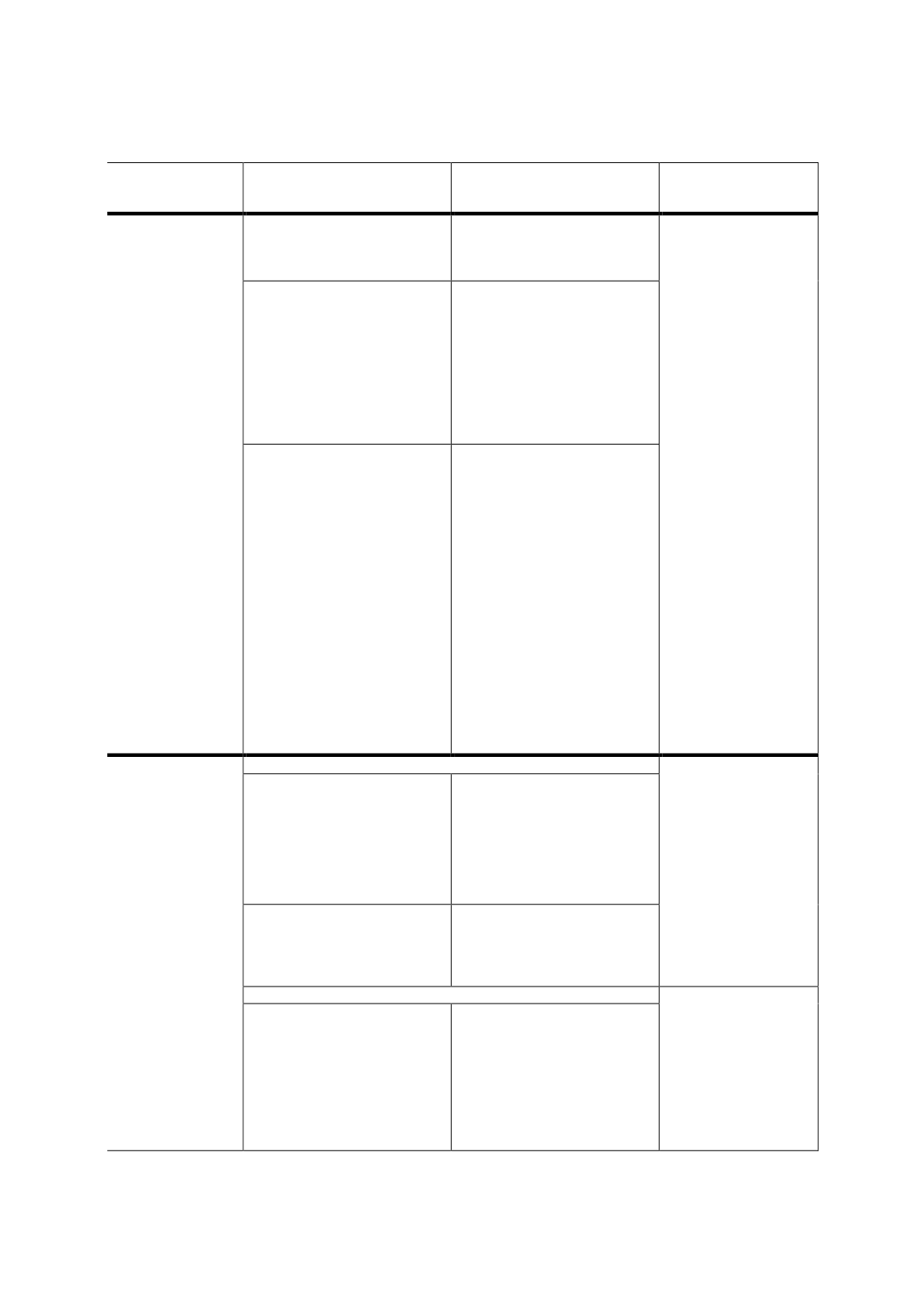
Stage of sukuk
market
development
Issues and challenges
Key recommendations
Rationale
prioritise raising funds
via sukuk instead of
bonds to finance their
budget deficits.
encourage
”crowding in”
instead of ”crowding
out”.
To increase funding
efficiency and
alleviate the
negative economic
and financial effects
of heftier
government debt,
including the
crowding out of
banking credit to the
private sector.
Shortage of long-term
sukuk issues that cater to
the needs of long-term
investors such as pension
funds as well as insurance
and
takaful
companies.
To issue sukuk with
longer maturities,
especially by government,
to fund infrastructure
projects and provide the
necessary benchmark
yield curves that will
enable local corporations
to raise longer-term
sukuk.
Lack of diversification
in investor base –
concentration on
banking institutions
with less
intermediation from
NBFIs.
To increase demand from
various investors,
including:
-
Institutional investors
that need long-term
investments, such as
insurance companies
and pension funds.
-
High–net-worth
individuals who are
currently investing
more in equities and
real estate.
-
To encourage
sovereign wealth funds
to invest in their
domestic bond
markets.
-
Retail investors.
Developing
(Intermediate and
Beginner)
(examples of OIC
countries include
Indonesia and
Turkey)
Legal and regulatory framework
To provide a conducive
environment for the
ICM to prosper.
Local companies prefer to
issue FCY conventional
bonds to fulfil their
financing needs due to the
macroeconomic
conditions of the market
(i.e. high inflation rate and
volatile local currency).
At the government and
monetary policy levels,
efforts should be made to
improve/attain
macroeconomic stability.
Limitations and/or
restrictions within the
capital markets.
To revise some
regulations to allow
multinationals to issue
LCY and FCY sukuk in the
domestic market.
Market and infrastructure development
To create more efficient
capital-market
intermediation and
encourage the issuance
of more sukuk as a
credible source of
funding.
To level the playing
field between sukuk
Lack of awareness among
key market stakeholders:
service providers (e.g.
investment banks,
securities companies,
advisory houses, brokers,
traders, rating agencies),
banking institutions and
NBFIs.
To increase knowledge on
the importance of sukuk
as an alternative source of
funding, and promote
market awareness on the
process of structuring,
issuing and investing
among different market
segments.