Child and Maternal Mortality
in Islamic Countries
75
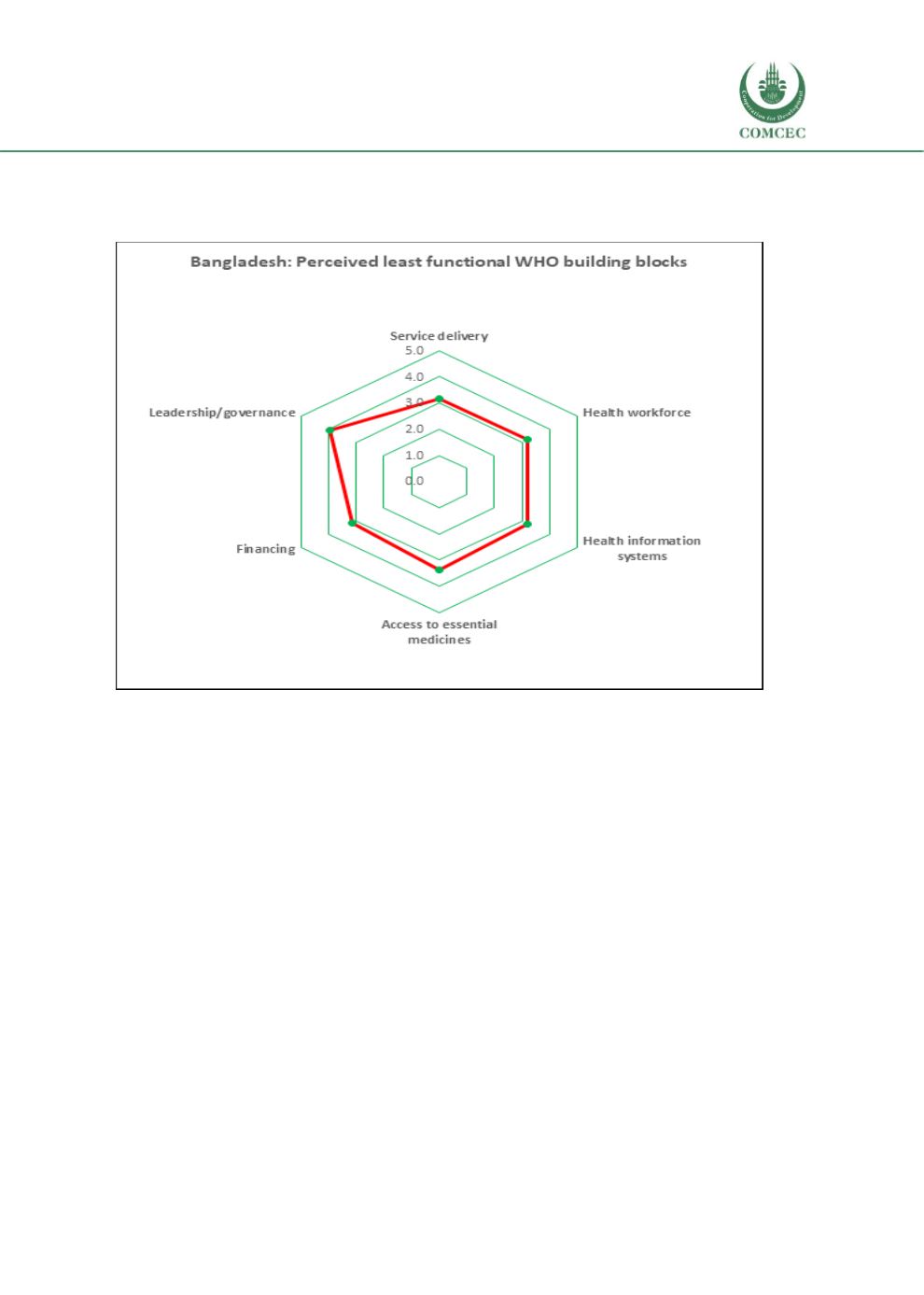
Figure 3.21. Perceived least functional WHO building blocks, Bangladesh
(Score: 1= Best functioning; 2= Better functioning; 3= functioning well; 4= Somewhat
functioning; 5= worst / not functioning)
Perceived barriers to accessing healthcare services
The responses to barriers to access were codes as follows: 1= Most significant barrier; 2= Second
most significant barrier; 3= Moderate barrier; 4= Somewhat of a barrier; and 5= Not a barrier.
Physical accessibility (mean score of 4.7) was considered the least important barrier, and the
quality of care (mean score of 1.4) was considered as the most pronounced barrier to access.
The shortage of health staff (2.0) was considered the second most important barrier to access
to care. Financial affordability (2.8) was considered not a significant barrier to access health care
services. The supply of essential drugs (3.6) and acceptability of health care services (3.4) was
perceived as moderate barriers.