Child and Maternal Mortality
in Islamic Countries
71
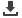
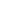
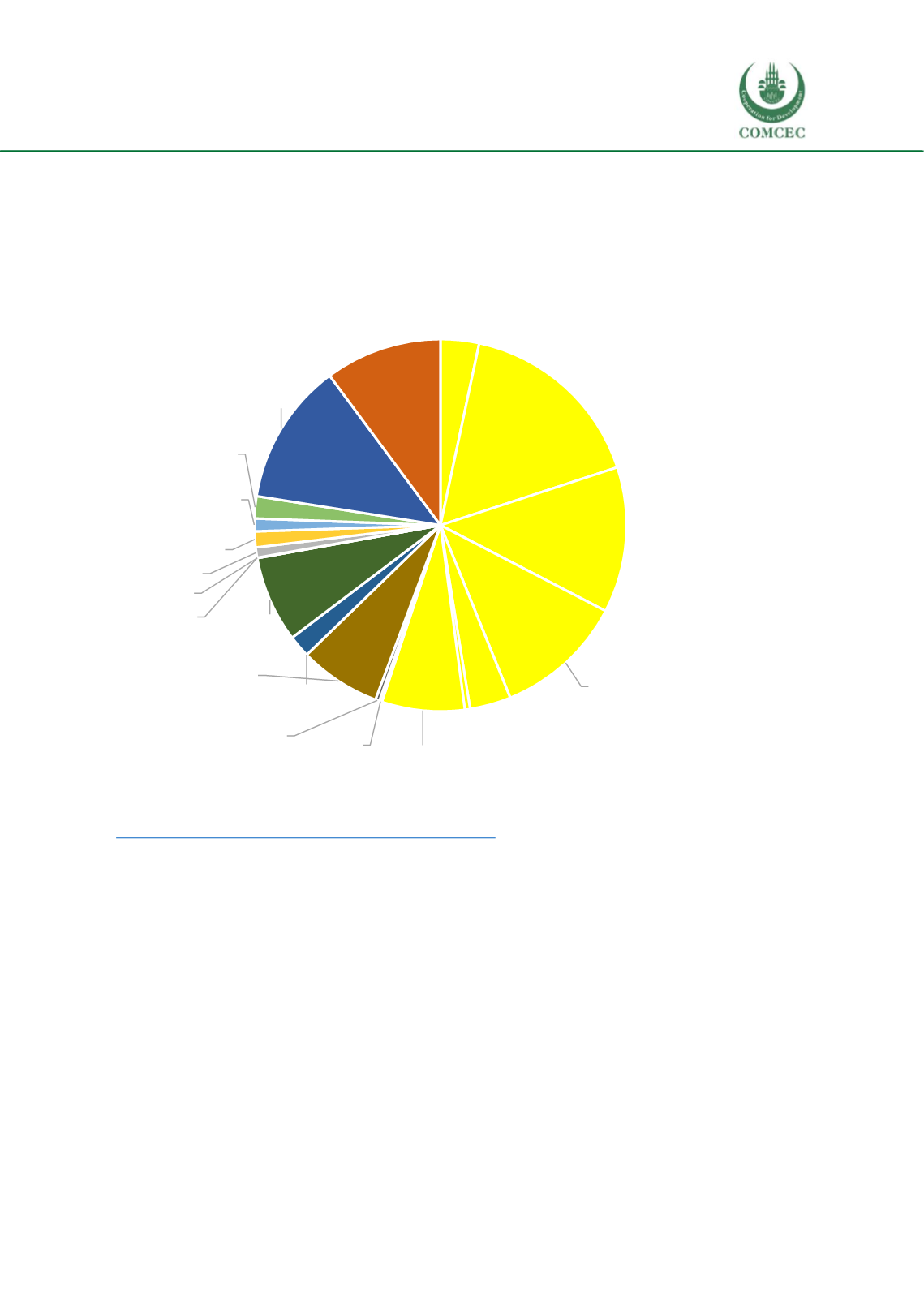
Figure 3.19 shows the causes of under-five mortality in Bangladesh in 2017. Over half (57%) of
under-five deaths in Bangladesh occurred in the neonatal period. The top three leading under-
five causes are preterm birth complications (20.5%), intrapartum related events (15.7%), and
pneumonia (15.4%).
Figure 3.19. Causes of under-five mortality, Bangladesh, 2017
Data source: Maternal and Child Epidemiology Estimation and Global health Observatory, available at
https://www.who.int/gho/child_health/mortality/causes/en/3.1.2. Progress in MNCH Care Indicators in Bangladesh
Bangladesh has experienced considerable progress in MNCH care utilization indicators in the
last three decades. Any ANC visit rate has increased from 27.3 % in 1993-94 to 78.5% in 2014
(BDHS 2017 data are publicly not available yet). However, the use of at least four ANC visits,
recommended by the WHO, was much lower. ANC4+ visits rate has increased from 5.5% to
31.2% during the same period (1993-94 to 2014).
Skilled birth attendance rates increased predominately since 2004 – from 13.2% to 42.3% in
2014. Deliveries at health facilities increased from 9.9% to 37.6% during this period. The
IHME/GBD projected that the SBA rate in Bangladesh will increase to 80% by 2030. Although c-
section was low in Bangladesh in 2004 (3.5%), there was a rapid rise in c-section in the
subsequent period. The c-section rate was 22.9% in 2014.
Pneumonia;…
Preterm birth
complications;
18,96
Intrapartum-
related events;
14,45
Sepsis or
menigitis; 12,85
Other; 4,08
Injury; 0,52
Congenital; 8,21
Tetanus;…
Diarrhoea;…
Diarrhoea; 8,07
Measles; 2,20
Injury; 8,55
Malaria;…
AIDS; 0,02
Meningitis;…
Preterm birth…
Intrapartum-
related events;
1,27
Congenital; 2,19
Other; 14,09
Pneumonia;
11,58
Deaths among children
aged
1-59 months (43%)
Neonatal deaths