Child and Maternal Mortality
in Islamic Countries
123
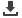
Figure 3.71: Domestic Government Expenditure and Health Prioritization (GGHE-D%GDP
and GGHE-D%GGE)
Source: WHO Global Health Expenditure Database
3.4.4. Lessons learned from Iraq
The maternal mortality and neonatal mortality rates are below the level of most OIC countries.
However, the most recent MMEIG/WHO estimates (September 19, 2019) suggest that maternal
mortality has not reduced in Iraq between 2000 and 2017.
78
According to the key informants, the governmental spending on health in Iraq is the lowest in
the region and investment in health is not in line with the state vision to reform the health
system which has led an increased inequality among citizens in access to health services.
According to the key informants, the budget for medicines and medical supplies are insufficient
to cover the total need even of the essential medicines. Lack of funding has led to significant gaps
in the provision of curative, preventive and infrastructure services from hospitals and primary
health care centers. There is a lack of adequate health promotion and health education, with a
low allocated budget for such services.
Many women and newborns do not receive quality maternal and child care, even when they are
able to access health facilities before, during, and after pregnancy and childbirth. This may be
because of a lack of health staff, especially doctors. Doctors are not available in about 50 % of
primary health care centers and only 6.2 % of physicians are working in PHC centers. According
to the key informants, there is a shortage of doctors in the country, which is because of the poor
coordination between MOH and the Ministry of Higher Education / Academia. So, colleges of
medicine in their plans do not satisfy the MOH requirements of specialized doctors in terms of
required numbers to be graduated every year. Uneven distribution of staff and lack of
availability of professionals in remote and rural areas were also mentioned as a barrier of
receiving MNCH services with quality of care. There was no functional referral system to ensure
a continuum of care at different levels.
Another challenge is the weakness in the health information system where there is no effective
electronic program to collect information and some of the information collected is inaccurate
and this information not used for the most part to plan and formulate health policies.
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
0,0%
1,0%
2,0%
3,0%
20002001200220032004200520062007200820092010201120122013201420152016
OOPS%CHE (Red Bars)
GGHED%GDP (Green Line)
Iraq: Domestic Government Expenditure and Out of
Pocket Spending (GGHE-D%GDP and OOPS%CHE)