39
One can see that most of the African group of OIC countries display high or very high risk of
catastrophic expenditure for surgical care. Only in Gabon, the Gambia and Mozambique less than
58% of the population is at risk of catastrophic expenditures. In contrast, in Asia, no country has
more than 39% of the population at risk of catastrophic expenditures.
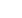
Table 6outlines the historical trends in indicators related to financial accessibility of health
services in OIC countries. The data confirms that current health expenditure per capita had
consistently increased in OIC countries and in the three OIC subgroups over the 20-year period.
The out-of-pocket spending data for OIC subgroups reported in
Table 6show a phenomenal
increase in such spending over the same period.
Table 6: Trends in financial access to care in OIC countries
UHC
service
coverage index
Low
OIC
average
High
African
group
Arab
group
Asian
group
2015
29
49.2
72
39.4
62.5
51.0
(Chad)
(Oman)
Out-of-pocket
expenditure
per capita, PPP
(current
internat. $)
Low
OIC
average
High
African
group
Arab
group
Asian
group
2011-2015
4.4
183.6
936.7
96.1
273.4 186.6
(Mozambique)
(Azerbaijan)
2006-2011
161.3
83.1
211.5 175.0
2001-2005
124.6
96.2
167.3 119.6
1996-2000
83.5
47.7
143.8
76.4
Risk
of
catastrophic
expenditure
for
surgical care (% of
people at risk)
Low
OIC
average
High
African
group
Arab
group
Asian
group
2011-2015
1.4
44.7
91.6
62.4
36.9
38.9
(Turkey)
(Niger)
2006-2011
54.1
66.4
38.2
54.1
2001-2005
56.6
59.8
45.2
59.4
1996-2000
-
-
-
-
Proportion
of
population
spending > 10% of
household
consumption or
income on OOP
(%)
Low
OIC
average
High
African
group
Arab
group
Asian
group
2011-2015
1.8
8.9
26.2
6.8
26.2
5.7