84
3.1.5.
Regression Analysis of the Determinants of Learning Outcomes
The review of the national policy documents and the international academic literature on school
effectiveness suggests that student learning in Jordan is not only low, there is also significant
inequality in access to quality education. The former is owing to system-wide factors while the
latter arises because of advantages enjoyed by children from high SES families. Therefore in this
section, the determinants of student achievement in Jordan are formally analyzed using PISA
2012 data.
18
To disentangle the influence of different types of covariates, multivariate
regression analysis is undertaken. The regression model is conceptualized to account for
personal, family-specific and institutional factors. The latter encompasses school resources as
well as policies.
We use PISA data for two reasons. First, it assess student performance in three domains whereas
TIMSS is only limited to mathematics and science. Second, TIMSS data set doesn’t have reliable
measures of family backgrounds. While this is available for grade 4 students, Jordan doesn’t
participate in that version of TIMSS. In contrast, PISA data set includes a wide range of indicators
capturing household socio-economic status including household wealth.
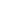
Table 3.1.2: Determinants of Student Achievement in Math, Reading and Science, PISA 2012
VARIABLES
Reading
Math
Science
Household wealth: : 2nd quartile
6.505
3.421
5.715
(3.969)
(3.774)
(3.841)
Household wealth: 3rd quartile
14.72**
12.16**
13.07**
(3.951)
(3.673)
(3.912)
Household wealth: top quartile
9.815*
9.681*
10.73*
(4.417)
(4.026)
(4.491)
Girl
61.47**
9.499+
30.05**
(5.953)
(5.561)
(5.671)
Age
14.93**
14.07**
17.23**
(4.203)
(3.576)
(3.906)
Attended pre-school
31.60**
25.90**
24.95**
(3.727)
(3.027)
(3.487)
Learning minutes (in language lessons)
-0.0102
-0.00632
0.0170
(0.0254)
(0.0289)
(0.0257)
Proportion of certified teachers
-0.871
-1.202
-7.227
(7.934)
(7.113)
(6.201)
Parental pressure: low
7.961
6.507
10.51
(8.731)
(8.076)
(7.512)
Parental pressure: absent
8.823
1.256
8.215
(8.882)
(8.164)
(6.960)
Small town
2.701
-2.651
-2.383
(9.030)
(8.440)
(9.598)
Town
10.54
5.542
11.43
(9.966)
(9.253)
(9.909)
City
18.30+
14.16+
9.745
(9.400)
(8.458)
(9.181)
Large city
27.21*
26.56*
21.74*
(11.25)
(12.43)
(10.65)
18
For existing analysis based on older rounds of PISA data for Jordan, see World Bank, (HDNED, 2008) “Using
PISA to Understand the Determinants of Learning in the Middle East and North Africa Region,” The World
Bank, HDNED.