
Education of Disadvantaged Children in OIC:
The Key to Escape from Poverty
121
3.3 JORDAN
Overview
Country Context
Economy:
Over the past 10 years, Jordan has pursued structural reforms in education, health, as
well as privatization and liberalization. However, its economy has been significantly affected by
external crises such as the Iraq crisis (2003), the 2008 financial crisis and finally the Syria crisis
since 2011. The Iraq and Syrian crises affected the economy through disrupted trade routes, lower
investments and lower tourism inflows. The 2008 financial crisis worsened the existing budget
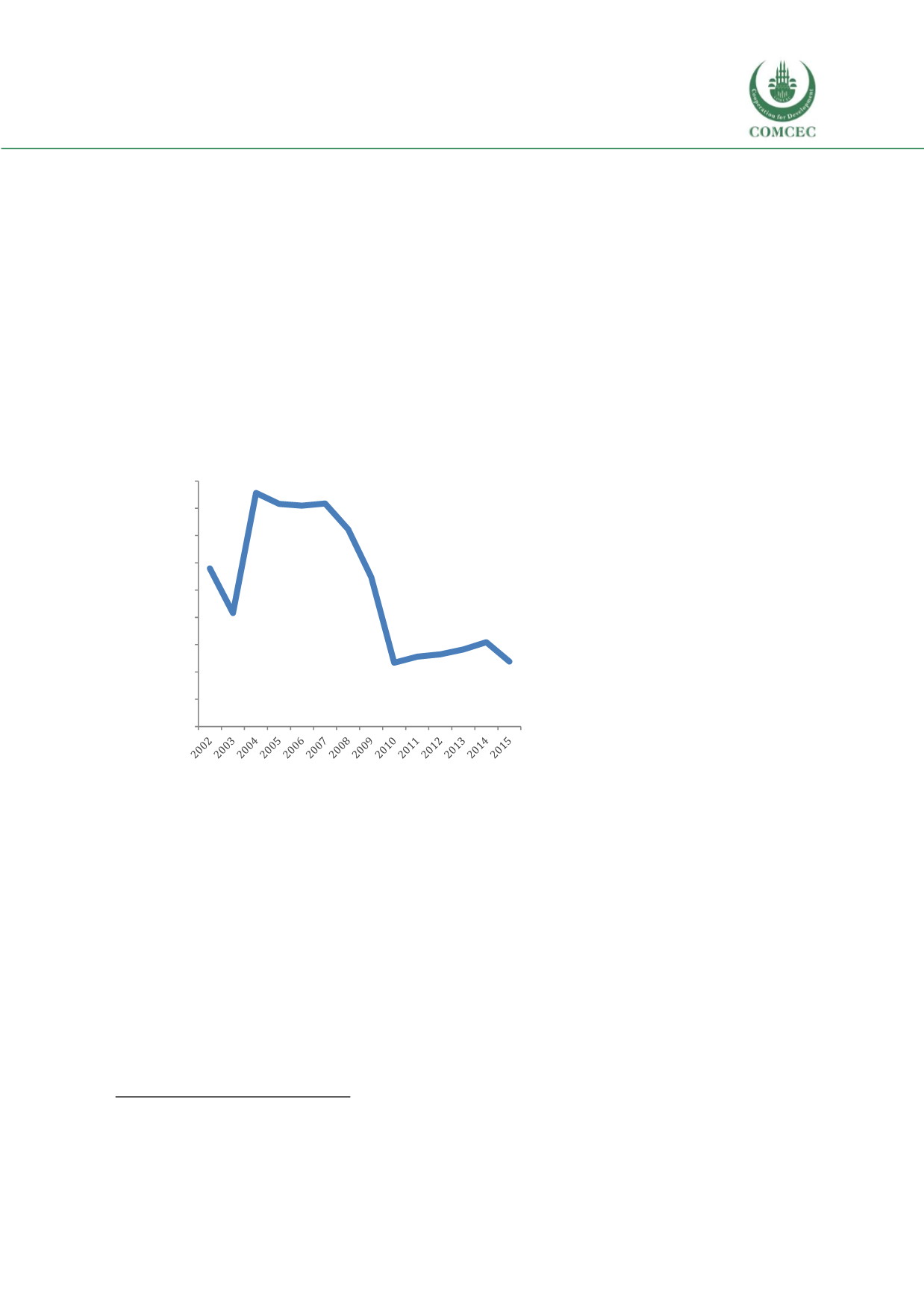
shortages as GDP growth rates plummeted from around 7.2% in 2008 to 2.3% in 2010.
The Syrian crisis in 2011 has not
allowed the country to bounce
back to pre-financial crisis GDP
growth
rates
and
Jordan’s
economy continues to face low
growth (
see
Figure 47 ), a
dependency
on
grants
and
remittances
from
the
Gulf
economies as well as high
unemployment and pressures due
to its scarce natural resources.
As
Syrian refugees in urban areas are
granted access to public services
(including
health,
education,
shelter, water and electricity), the
pressure on national resources
(including water in refugee camps)
and subsidized services has dramatically increased.
Fiscal and monetary policies have been
tightening in an effort to reduce the debt-to-GDP ratio as part of an IMF-required fiscal reform
plan, which does not facilitate the efforts needed to stimulate job-generating growth. In terms of
poverty, the rate of child poverty is on the increase, reaching 19% in 2012
331
.
Administration:
Jordan is divided into twelve governorates (
muhafazah
) by the administrative
divisions system of the Ministry of Interior. Each is headed by a governor appointed by the King.
In 1994, four new governorates were created: Jerash, Ajloun, Madaba and Aqaba. Governorates
are further subdivided into districts (
liwa
) and often into sub-districts (
qda
). The 12 governorates
are Capital (Amman), Irbid, Zarqa, Balqa, Mafraq, Jerash, Ajloun, Madaba, Karak, Tafilah, Ma’an
and Aqaba. Geographically, the governorates of Jordan are located in one of three regions: the
331
UNICEF (2014)
Figure 47 Jordan GDP growth (annual %)
Source: World Bank World Development Indicators
5,8%
4,2%
8,6%
8,2%8,1%8,2%
7,2%
5,5%
2,3%
2,6%2,7%2,8%
3,1%
2,4%
0,0%
1,0%
2,0%
3,0%
4,0%
5,0%
6,0%
7,0%
8,0%
9,0%
GDP growth (Annual %)
















