Increasing Broadband Internet Penetration
In the OIC Member Countries
26
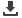
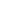
Figure 8: The regional effect of broadband on job creation according to different levels of
penetration
Source: Katz (2011)
These different effects can be explained by the fact that increased broadband deployment in
more advanced regions creates a "supply shock" within the context of companies who can
leverage technology to generate new businesses while yielding production efficiencies. In
contrast, in regions with lower broadband adoption, the increase in broadband penetration
leads to an initial substitution between capital and labor, in which the productivity generated
by the technology produces a decline in employment.
11
In the medium term, the increase in
adoption has a positive impact, which can be explained in terms of learning in the assimilation
of the technological input and the generation of innovations that create jobs. In other words, in
those regions lagging behind, the effect of broadband is increased productivity in the short
term and, as a result, the loss of jobs; in the medium and long term, innovation leads to job
creation.
In sum, while there is a strong consensus in the positive and statistically significant effect of
broadband on economic growth, when comparing findings across research, a number of
caveats need to be raised. First, broadband exhibits a higher contribution to economic growth
in countries that have a higher adoption of the technology (this could be labeled the "critical
11
This effect was alluded to by Gillett et al. (2006) in indicating, "broadband can facilitate the capital-labor substitution,
resulting in lower rate of employment growth.” Thompson et al. (2008) also mentions “it is possible that a substitution effect
between broadband and employment exists."
T+1
T+2
T+3
T+4
Economic Impact
HI
LO
GDP
Employment
T+1
T+2
T+3
T+4
Economic Impact
HI
LO
GDP
Employment(*)
High Broadband Penetration Regions
Low Broadband Penetration Regions
•
High economic growth initially,
diminishing over time ( supply shock
effect)
•
New Economic Growth (innovation,
new services)
•
High stable economic growth ( catch
up effect)
•
Capital/labor substitution limits
employment growth ( productivity
effect )
Increase in
BB
penetration
Increase in
BB
penetration
(*) Results are at a low significance level