Increasing Broadband Internet Penetration
In the OIC Member Countries
22
Finally, the introduction of broadband can also help to reduce the time otherwise required for
an effective job search, allowing underemployed workers to look for full-time work using
broadband services. This increase in efficiency leads to a reduction in unemployment periods
and generates an increase in the migration of underemployed workers to full-time positions,
which, in turn, results in higher labor income. In other words, reduced transaction costs
related to finding employment can ultimately result in higher income (with less search time
required, the underemployed can find full-time work).
Broadband impact on consumer surplus
There are some specific economic effects of broadband that are not necessarily captured by
economic growth or employment creation. This is the case of consumer surplus, which has also
been found to be affected by the positive externalities of broadband. Consumer surplus is
defined as the amount that consumers benefit from purchasing a product for a price that is less
than what they would be willing to pay. In other words, consumer surplus is the utility gain by
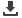
consumers due to prices that are lower than their reservation prices. In figure 5 the consumer
surplus is the area between the demand curve and the market price. The larger the area under
the curve is, the more utility consumers derive.
Figure 5: Conceptual representation of consumer surplus
Source: adapted from Katz et al. (2008b)
Consumer surplus may change over time because of two reasons. The first one is an outward-
shift of the demand curve, and the second is a price reduction. The price reduction may result
from productivity gains and competition. More competition and market saturation force
producers to reduce prices. These two developments are responsible for increases in
consumer surplus. As indicated in figure 5, the dark grey area represents the initial consumer
surplus at t=0. The shift of the demand curve at t=1 results in an additional consumer surplus
(light grey area). The whole consumer surplus in period 1 is the sum of the dark and light gray
areas.