Planning of National Transport Infrastructure
In the Islamic Countries
55
The involvement of private sectors in NTI planning in Kazakhstan is high, not only in the
implementation phase (see section Development Funding here below) but already in the
planning phase. This is especially the case for national or state-owned companies related to
infrastructure development like Kazakhstan Temir Zholy (the national railway company). This
institution stipulated that they have significant contribution in forming NTI planning policies in
Kazakhstan16. While the involvement of private sectors is high, that of academia is another
story. The involvement of academia in NTI planning process in Kazakhstan is very low if not
zero
17
.
Development funding
The activities and investment projects of the Program are financed by the National Fund of the
Republic of Kazakhstan, republican and local budgets, international financial institutions and
organizations and own funds of the national companies and development institutions as well as
private investment through PPP with the overall indicative amount of USD 23.2 billion. The
following is the proportion of each of these funding sources:
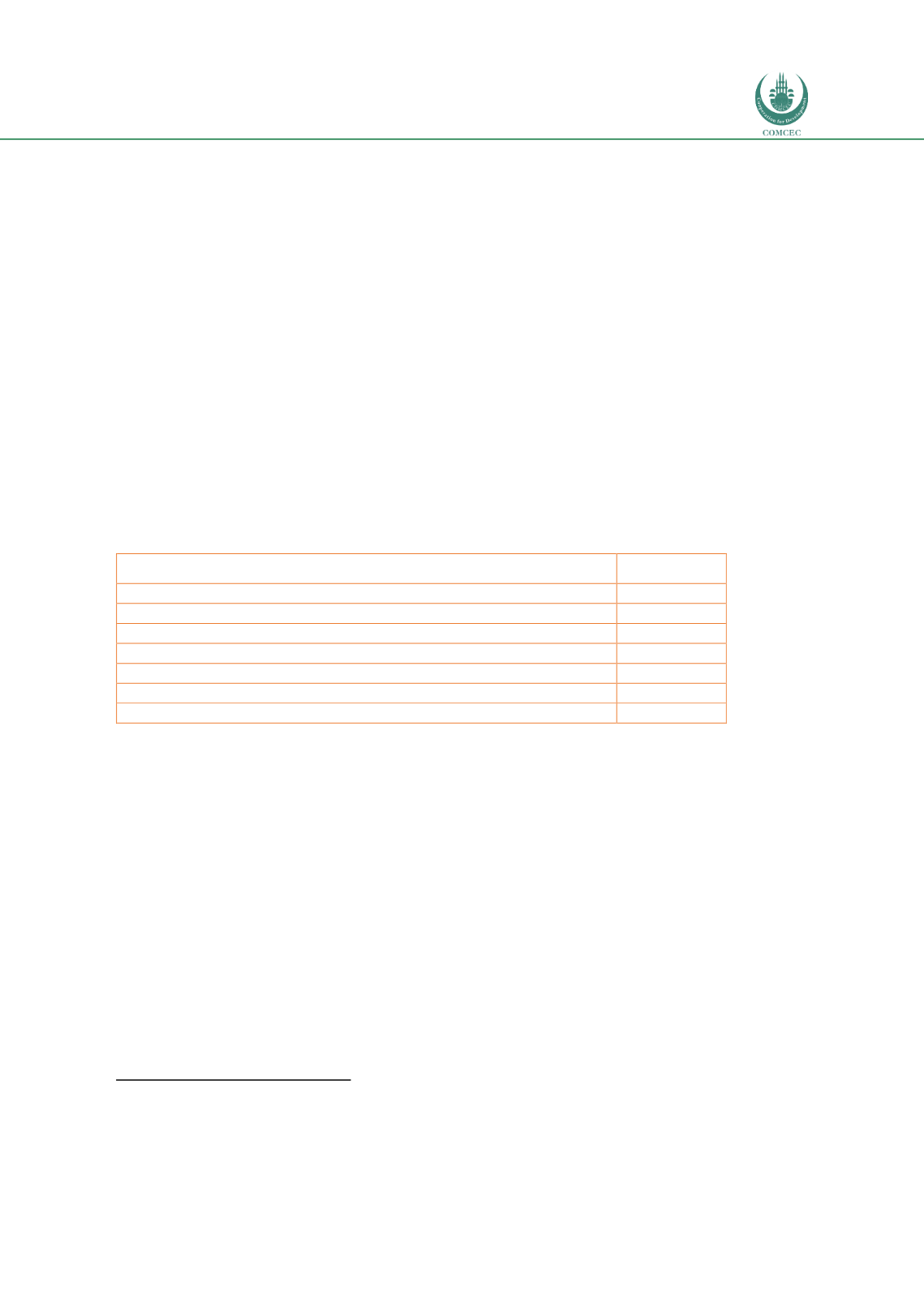
Table 6: Division of funding sources of the investment projects of the Program
Source of funding
Percentage
The republican budget
5.6%
National Fund
30.7%
The local budget
3.9%
The international financial institutions and organizations
51.5%
Own funds national companies and the development institutions
7.8%
Private investments and PPP
0.5%
Total
100%
Source: Nurly Zhol (2014)
The largest share of the funding is from the IFIs. Those who are active in the transport sector in
Kazakhstan include theWorld Bank, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the European Bank
for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD). These IFIs are mostly financing the development
of the CAREC corridors passing the territory of Kazakhstan.
The second largest funding is from the National Fund, while private investments and PPP still
have a very small contribution despite the political will to enhance private sector involvement
(see sectio
n 3.1.2 about the concession model in Kazakhstan).
Currently the only road user charges that can be considered to contribute to the financing of the
republican road network include transit fees for trucks, roadside advertising on republican
roads and toll revenue
1
. Fines for overloading on republican roads are also being introduced,
and should be included as republican road user charges. These road user charges currently
16
Based on a questionnaire survey conducted by Fimotions in 2018.
17
Based on an interview with University of Nazarbayev in 2018.