Improving Transnational Transport Corridors
In the OIC Member Countries: Concepts and Cases
133
corridor and hinterland will impact positively on these factors. The main question is whether
Africa really is a low-cost site from which to run a business. According to the World Bank
62
,
although data on production costs are not easily available, a number of reports and anecdotal
evidence clearly show that Africa is far from being a low-cost production site. A combination of
factors linked to the institutional and physical business environment make the African
continent one of the most expensive places in the world to produce. By some estimates as
much as 25 percent of sales of firms in some African countries are lost because of impediments
of the investment climate such as unreliable infrastructure, contract enforcement difficulties,
crime, corruption, and poor regulation. These losses are, at times, much higher than taxes paid.
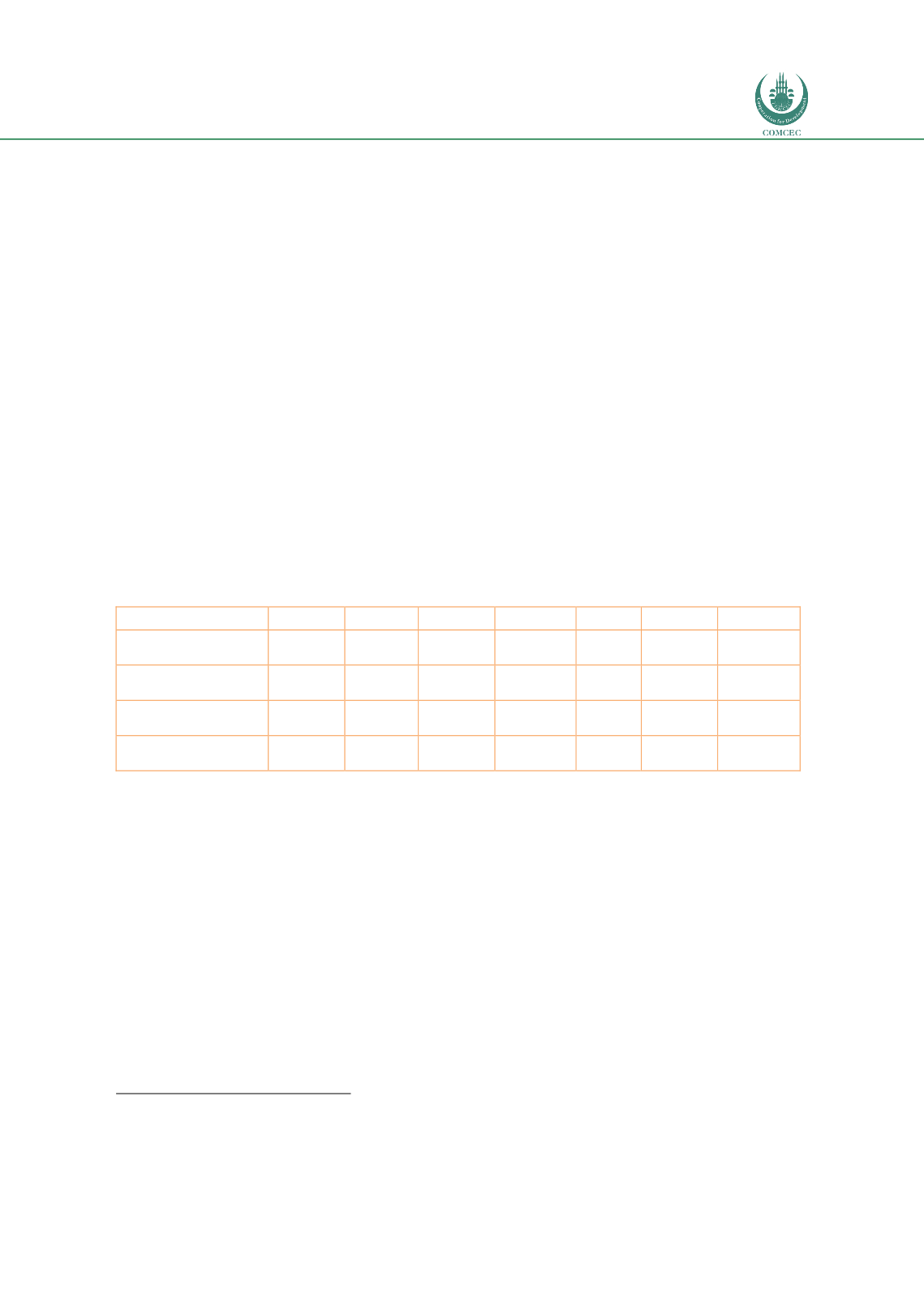
A compilation of prime costs in the economies of each corridor country is given in
Table 42.The cost of investment is indicated by the prevailing base interest rate in each country. Rates
are well above those in Europe and USA. Rates are lowest in Rwanda, a country that is making
rapid progress to reform and modernize but they are highest in the DRC, which has the least
reformist government. Labor rates in Africa are generally low at about 180 USD per month
(2008). However, value added and productivity is also low, making low labor rates costlier
than generally apparent. The rates shown in the table are current and indicate that African
labor rates are relatively low.
Table 42: Examples of prime costs in corridor countries
Cost Item
Uganda
Rwanda Burundi
Kenya
DRC
S. Sudan
Tanzania
Cost of investment -
Base Rate of Interest
11%
6.25%
7.17%
10%
14%
12.50%
12%
Median cost of labor
(USD net per hour)
0.4
0.65
0.43
1.26
0.64
0.35
0.92
Cost of industrial
land (USD per Ha)
650,000
620,000
N/A
650,000
850,000 N/A
640,000
Cost of energy
(USD per KWh)
0.15
0.22
0.11
0.03
0.048
0.42
0.17
Source: Fimotions (2017), from various sources.
Notes to table:
i.
Interest rates are current to 2017
ii.
Cost of labor is inflated to current prices using latest exchange rates from latest available data
iii.
Industrial Land is generally close to the capital city
iv.
Energy prices are current to 2017
The cost of industrial land is rather similar in corridor countries, which may provide an early
sign of leveling due to improvements in accessibility since land prices and location are closely
linked. The price of energy varies a lot between TTCANC countries. The reasons is that energy
markets remain firmly controlled by government, transmission and distribution networks are
not linked and the energy sector is not commercialized / privatized. Agreements are in process
to commercialize and regionalize energy generation and supply networks.
62
http://siteresources.worldbank.org/EXTAFRSUMAFTPS/Resources/chapter4.pdf