Improving Transnational Transport Corridors
In the OIC Member Countries: Concepts and Cases
98
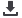
Figure 32: CAREC Overall Institutional Framework
Source: CAREC 2020 (2012).
The MC provides mainly an overall strategic guidance to the process of economic cooperation.
The SOM ensures the effective implementation of the policy decisions made by the MC. The
NFPs are responsible for effective coordination among government agencies and other parties
and for overseeing implementation of priority projects and initiatives. As such strong
institutional capacities are mandatory.
The institutional arrangements of CAREC are established based on the flexibility and
pragmatism responded to the countries’ unique needs and circumstances. On the other hand,
this principle has caused countries to be less
forthcoming in manifesting their commitment to the
Program.
Country plans for infrastructure development are not always consistently aligned
with those of CAREC
37
. Despite this, CAREC has a strong institutional framework that plays a
very important role in the success of the CAREC corridors. According to the experts at the
CAREC secretariat, the main success factors can be formulated as follows:
1.
Cooperative Approach
For projects funding, CAREC uses the “2+X” principle, which means that a project can be
classified as a CAREC regional project, be it investment or technical assistance, if it
involves at least two CAREC countries
38
. CAREC countries must follow the said
overarching goals in implementing projects.
37
An institutional Framework for Facilitating Economic Cooperation in the Central Asia Region, CAREC.
38
CAREC Secretariat (2017).
(MC)
(TSCC)
(CCC)
(TPCC)
(ESCC)
(SOM)
(NFPs)