Improving Transnational Transport Corridors
In the OIC Member Countries: Concepts and Cases
97
4.4.2.
Political and Institutional Factors
Transport Strategies and Planning
In reviewing the national transport strategies and plans of each country, the most important
aspect to determine is the extent to which international transport and corridor development
features in them. The transport master plans of Afghanistan and Tajikistan clearly indicate
policy actions to remove physical and non-physical barriers to trade.
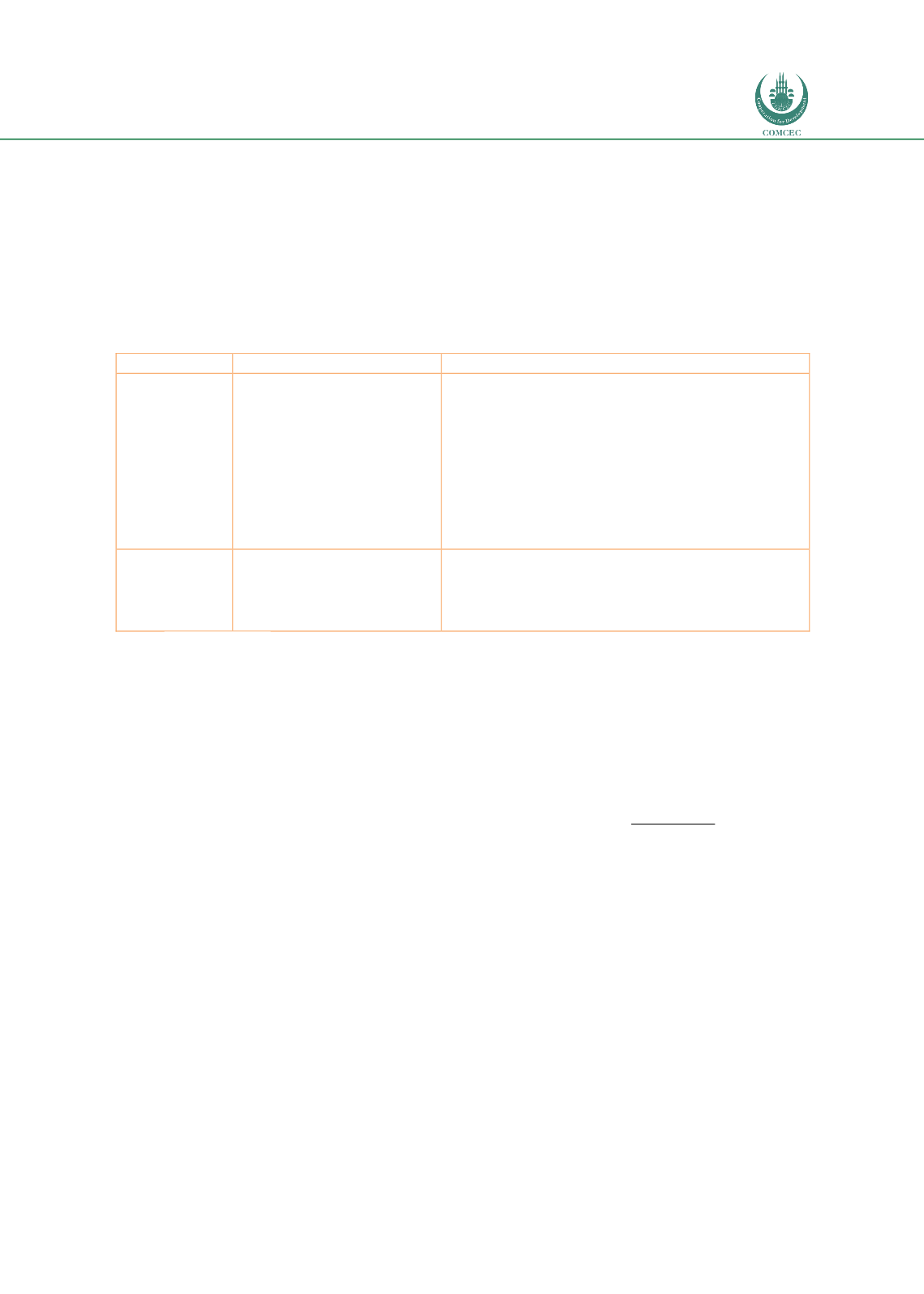
Table 21: Corridor Features in National Transport Plans of Corridor Countries
Country
Document reviewed
Transport and corridor development features
Afghanistan
Afghanistan Transport
Sector Master Plan Update
(2017-2036)
-
The needs to improve the performance of
transport and trade logistics and recommends
an assessment of BCP infrastructure in addition
to BCP operations.
-
Policy actions required to develop a seamless
intermodal network, to introduce a single
access point for administrative procedures, and
to encourage foreign vehicle transit through
adequate transit fees
Tajikistan
Developing Tajikistan’s
Transport Sector –
Transport Sector Master
Plan (ADB)
-
Rehabilitation of CAREC corridor 3b as one of
the road investment plans
-
Harmonization of border-crossing procedures
-
Implementation of single-window scheme
Source: Fimotions (2017).
No information can be found with regard to Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, and Uzbekistan.
However, considering the maturity of the CAREC secretariat and its institutional frameworks
(see here below), it is very likely that these countries include international transport corridor
features in their national transport strategies and plans.
Institutional Frameworks
CAREC has an Overall Institutional Framework (OIF) provides the mechanism for guiding,
coordinating, and overseeing the CAREC program, supported by the coordination function of
the CAREC Secretariat and the technical and financial support from the multilateral
institutions (Asian Development Bank, 2012). These multilateral institutions are the ADB,
EBRD, IMF, IsDB, UNDP, and the World Bank.