Muslim Friendly Tourism:
Regulating Accommodation Establishments
In the OIC Member Countries
77
C.
Certification Process
There are several key steps, which governments follow in establishing the certification
process for mainstream and MFT hospitality standards. However, there are certain gaps and
opportunities for improvement for the MFT certification process. They are addressed in full
detail in the recommendations section, but are summarized in the table below.
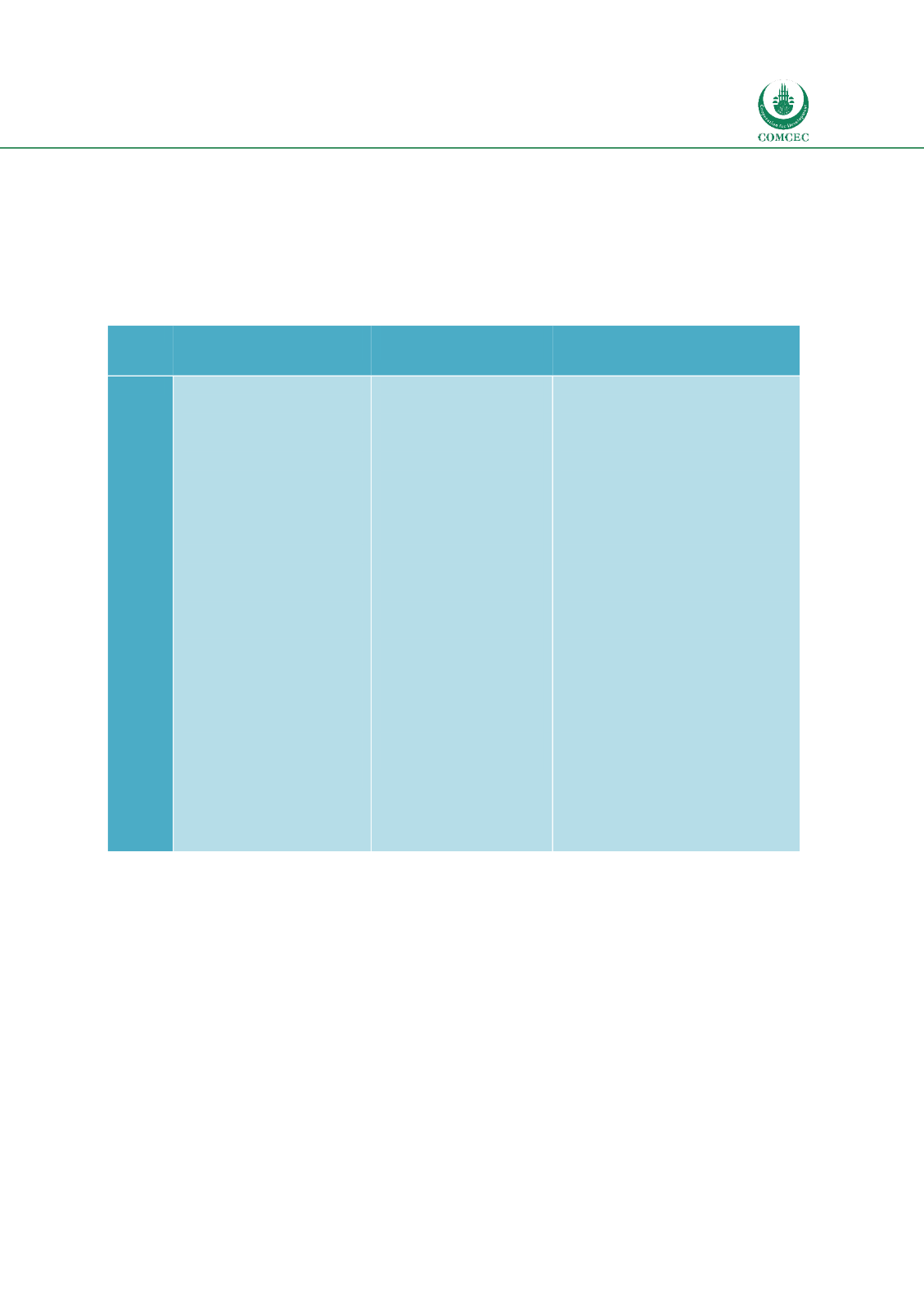
Table 19: Certification Process Steps for Government Standards
Mainstream Standards
MFT Standards
Gaps & Opportunities for
Improvement in MFT Standards
Steps
Self-evaluation against
criteria
Submit application to
certifying body
Pay fees
Certifying body audits
facility and prepares audit
report
If facility passes the audit,
it is awarded certification
If accommodation facility
does not pass the criteria,
it implements corrective
action and is re-audited
and if it passes receives
certification
Mystery guest inspections
are administered ad hoc
Certification is renewed
annually, every two,
three, or five years
depending on certificate
Submit application
Complete
documentation
Certifier trains internal
auditors
Implement Halal
standard requirements
Audit verification
invitation
Certification audit
If satisfactory, certifier
drafts audit report
Audit verification by
verification commission
If requirements are
fulfilled, Halal certificate
is provided
In case audit result is
unsatisfactory, hotel
removes deficiencies
and is re-audited
Standard setting body often also
provides certification which is a
conflict of interest
Certifiers often also provide
training to accommodation
facilities, which is a conflict of
interest
A Standard Operating
Procedures (SOP) document for
certifiers is often missing
Self-evaluation as an initial step
Administering mystery guest to
monitor compliance
Training on internal MFT
compliance should be extended
to all staff level, with depth
suited to each person’s
responsibility towards MFT.
Training should not just be
limited to auditors.
Source: DinarStandard
5.2.2 Private Standards
A.
How standards are developed
There are several key steps, which private entities follow in establishing mainstream
hospitality standards, which when compared to the steps for establishing MFT standards,
highlight a number of gaps and opportunities for improvement for MFT standards.
Some of the gaps are similar to the ones identified in developing government standards such
as ensuring all stakeholders are involved, while others are unique to private standards such
as obtaining government buy-in. The full list of gaps and opportunities in establishing private
standards is below.