Destination Development and
Institutionalization Strategies
In the OIC Member Countries
31
and local level are more involved with industry stakeholders in terms of providing them with training,
consultations and help in product development.
95
In the context of the stakeholder structured interviews conducted within the scope of this study,
respondents were asked to identify the responsibilities and tasks undertaken by DMOs operating within
their destinations. Most respondents identified product development, destination promotion, industry
support, research, and crisis management as some of the tasks primarily undertaken by DMOs on the
national level. Distribution support, pricing guidance, visitor experience management were identified by
many respondents as tasks performed on both the national and local levels. The task of stakeholder
coordination was identified as one of the tasks performed by DMOs at all national, regional and local levels
by some respondents. Respondents made a number of recommendations for improving DMO performance
of their role including creating formal platforms and think tanks to ensure stakeholder involvement in
decision-making and planning, providing support and incentives in areas of product development, and
minimizing bureaucratic procedures to make DMOs more adept in facing changes in the tourism industry.
2.4. Funding Models and Sources for DMOs
Sustainable funding is considered one of the important challenges for DMOs that can affect its spending on
needed activities and as a result their effectiveness in terms of ensuring destination competitiveness, as
such most DMOs seek diversification in funding and revenue streams fromboth public and private sources.
There are four funding models adopted by destination management organizations; the appropriation, the
cost recovery, the co-funding, and the industry-led models.
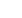
The following figure displays the various funding models and the public and private funding sources
available to DMOs for financing their operations and activities. As the table shows, the appropriationmodel
and the cost recovery and industry-led models occupy the ends of the spectrum with different funding
sources; with the appropriation model mainly depending on public funding as opposed to both the cost
recovery and industry-ledmodel depending on private funding. The co-fundingmodel occupies the middle
position in the spectrum as it combines the use of both public and private funding tools.
Figure 10: DMO Funding Models and Sources
Source: DinarStandard Analysis
95
A Practical Guide for Tourism Destination Management
(2007) (Rep.). WTO.
•
Hotel Room Taxes
•
Alternative Tax/Tourism Businesses Tax
•
National Taxes
•
State/Province Taxes
•
City/County Taxes
•
Sales Tax
Public Sources
Private Sources
•
Advertising Revenue
•
Membership Revenue
•
Partnership Revenue
•
Sponsorship Revenue
•
Visitor Information Centers
•
Commercial Activities
•
Tourism Improvement District (TID)
Appropriation
Industry-Led
Co-Funding
FundingModels
Cost Recovery
Types
Stakeholders
Activities
Funding
Governance Models