
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
78
According to the information available, 24 OIC MS have implemented CRM Strategy Policy and
Strategic Governance, commonly a copy of the general wording and general formulation of
standards recommended by the WCO, WTO and the CRM standards. In most cases, the CRM
Policy is adapted to the CDPS embedded RM functionalities – selectivity module for risk analysis.
4.3.1.1.3
OICMS International Agreements, Standards and Recommendations related to CRM
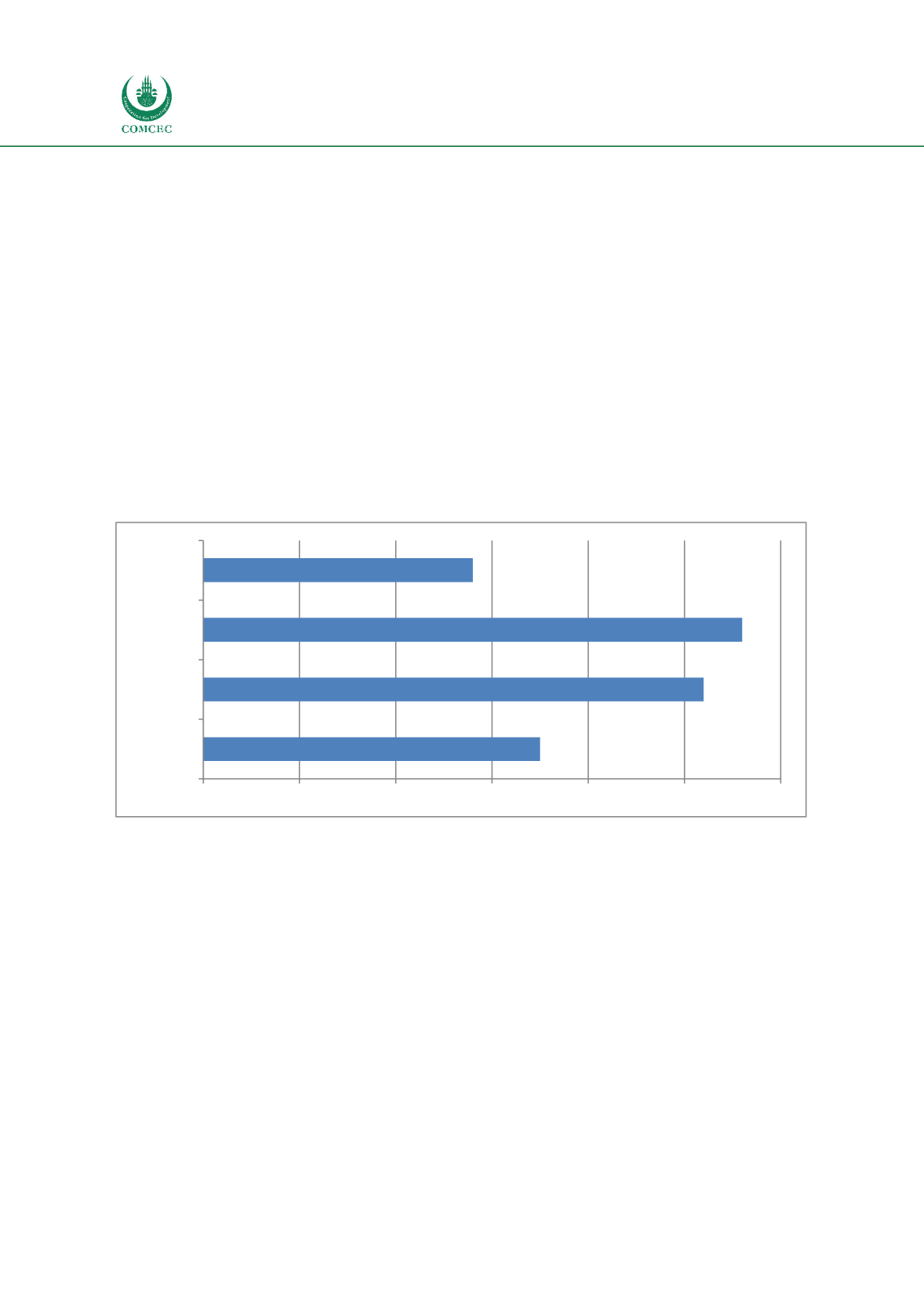
Apart from Surinam, all OIC MS are members of the WCO. 52 OIC MS ratified the international
WCO Framework of Standards (SAFE) instrument for a safer world trade regime (apart from
Algeria, Brunei Darussalam, Guyana, Palestine, Surinam, and Turkmenistan). 35 OIC MS are
party to the WCO International Convention on the Simplification and Harmonization of Customs
Procedures - Revised Kyoto Convention (RKC). The following OIC MS have not ratified the RKC
- Afghanistan, Brunei Darussalam, Chad, Comoros, Djibouti, Gambia, Guinea, Guinea - Bissau,
Guyana, Iraq, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Libya, Maldives, Mauritania, Palestine, Somalia, Surinam,
Syria, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan.
28 OIC MS ratified the WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement (Figure 24)
. Table 15 presents the OIC
MS International Agreements membership.
Figure 24: OIC MS International Agreements and Standards related to CRM
Source: Author’s compilation
35
52
56
28
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
RKC
WCO SAFE
WCO MS
WTO TFA
















