
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
159
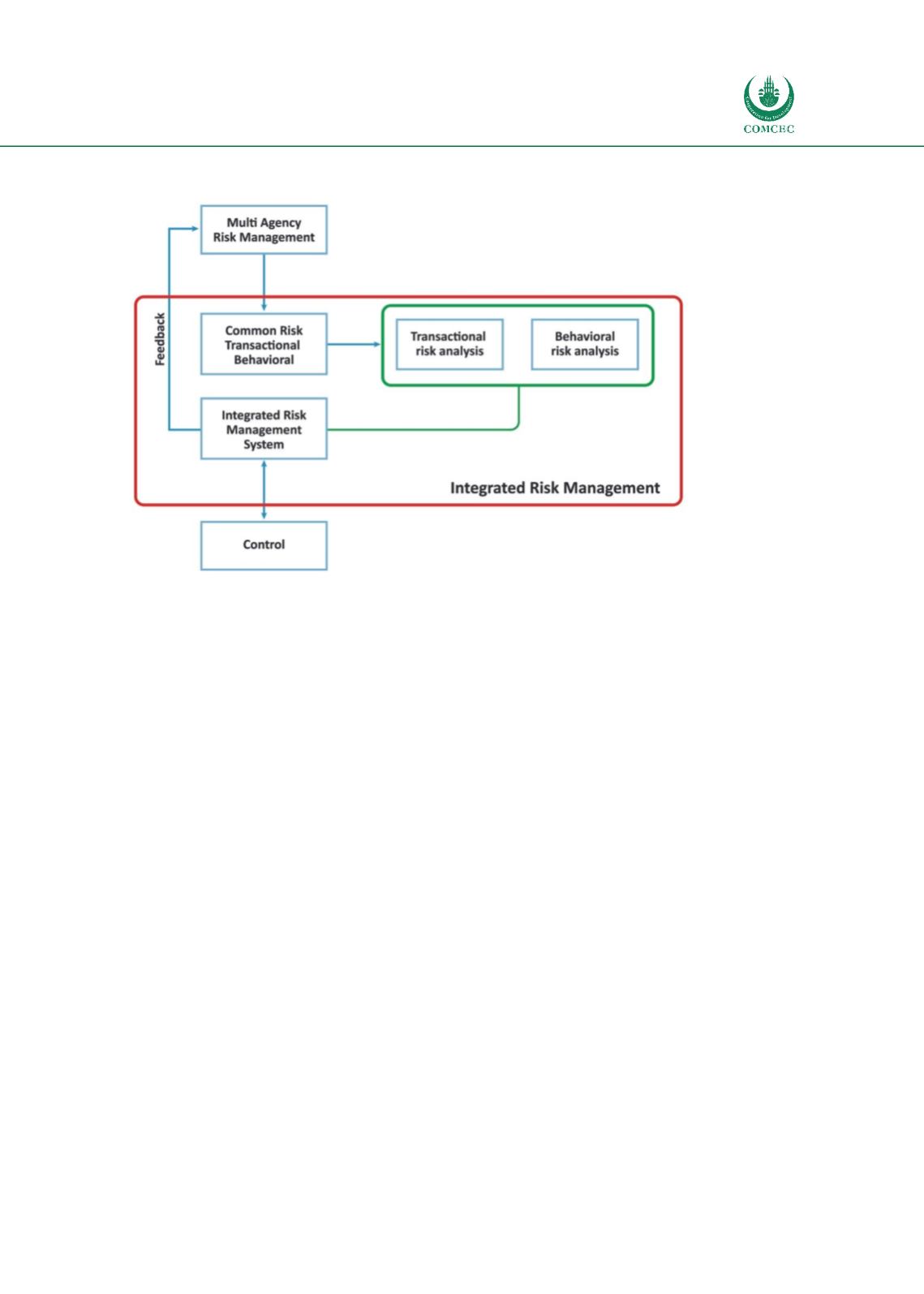
Figure 55: ICRM Conceptual Diagram
Author’s compilation
Attention should be paid to the heterogeneity of the IT Architecture of the participants in ICRM
- that consist of dissimilar or diverse IT systems. It is necessary to integrate these heterogeneous
environments into a single integrated system relying on hardware and software technologies
ensuring:
Use of highest ICT standards;
Flexibility and modularity;
Usability of legacy services/application and functionalities from ICRM participants;
Subsequent usability of newly developed services;
Based on the risk profiles developed in ICRM, control measures should be coordinated between
customs and other agencies;
High level of coordination of measures and activities in the system of ICRM;
Exchange of data and information between government agencies and institutions that
have competencies in the system of ICRM;
Coordination and assessment of situation in emergency cases at border crossings and
customs terminals;
ICRM is a base for coordination of cross-border cooperation.
One of the biggest benefits of the ICRM system is the feedback from control. This does not apply
only to cases of detected irregularities/non-compliance, but also to those cases in which the
control did not produce any results/findings. This applies not only to customs but to all agencies
involved in the import, export and transit procedures.
















